Broadness and specificity: ArdB, ArdA, and Ocr against various restriction-modification systems
- PMID: 37138625
- PMCID: PMC10149784
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1133144
Broadness and specificity: ArdB, ArdA, and Ocr against various restriction-modification systems
Abstract
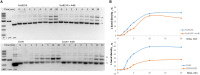
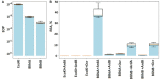
ArdB, ArdA, and Ocr proteins inhibit the endonuclease activity of the type I restriction-modification enzymes (RMI). In this study, we evaluated the ability of ArdB, ArdA, and Ocr to inhibit different subtypes of Escherichia coli RMI systems (IA, IB, and IC) as well as two Bacillus licheniformis RMI systems. Furthermore we explored, the antirestriction activity of ArdA, ArdB, and Ocr against a type III restriction-modification system (RMIII) EcoPI and BREX. We found that DNA-mimic proteins, ArdA and Ocr exhibit different inhibition activity, depending on which RM system tested. This effect might be linked to the DNA mimicry nature of these proteins. In theory, DNA-mimic might competitively inhibit any DNA-binding proteins; however, the efficiency of inhibition depend on the ability to imitate the recognition site in DNA or its preferred conformation. In contrast, ArdB protein with an undescribed mechanism of action, demonstrated greater versatility against various RMI systems and provided similar antirestriction efficiency regardless of the recognition site. However, ArdB protein could not affect restriction systems that are radically different from the RMI such as BREX or RMIII. Thus, we assume that the structure of DNA-mimic proteins allows for selective inhibition of any DNA-binding proteins depending on the recognition site. In contrast, ArdB-like proteins inhibit RMI systems independently of the DNA recognition site.
Keywords: ArdA; ArdB; RMI; antirestriction; conjugative plasmid.
Copyright © 2023 Kudryavtseva, Cséfalvay, Gnuchikh, Yanovskaya, Skutel, Isaev, Bazhenov, Utkina and Manukhov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Balabanov V. P., Kudryavtseva A. A., Melkina O. E., Pustovoit K. S., Khrulnova S. A., Zavilgelsky G. B. (2019). ArdB protective activity for unmodified λ phage against EcoKI restriction decreases in UV-treated Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol. 76, 1374–1378. 10.1007/s00284-019-01755-z - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

