Evaluation of learning outcomes of humanities curricula in medical students. A meta-review of narrative and systematic reviews
- PMID: 37138737
- PMCID: PMC10150636
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1145889
Evaluation of learning outcomes of humanities curricula in medical students. A meta-review of narrative and systematic reviews
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the expected learning outcomes of medical humanities subjects in medical studies curricula. To connect those expected learning outcomes with the types of knowledge to be acquired in medical education.
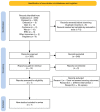
Methods: Meta-review of systematic and narrative reviews. Cochrane Library, MEDLINE (Pubmed), Embase, CINAHL, and ERIC were searched. In addition, references from all the included studies were revised, and the ISI Web of Science and DARE were searched.
Results: A total of 364 articles were identified, of which six were finally included in the review. Learning outcomes describe the acquisition of knowledge and skills to improve the relationship with patients, as well as the incorporation of tools to reduce burnout and promote professionalism. Programs that focus on teaching humanities promote diagnostic observation skills, the ability to cope with uncertainty in clinical practice, and the development of empathetic behaviors.
Conclusion: The results of this review show heterogeneity in the teaching of medical humanities, both in terms of content and at the formal level. Humanities learning outcomes are part of the necessary knowledge for good clinical practice. Consequently, the epistemological approach provides a valid argument for including the humanities in medical curricula.
Keywords: humanities; learning outcomes; medical education; undergraduate; university teaching.
Copyright © 2023 Coronado-Vázquez, Antón-Rodríguez, Gómez-Salgado, Ramírez-Durán and Álvarez-Montero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sánchez González MA. El humanismo y la enseñanza de las humanidades médicas. Educ Med. (2017) 18:212–8. doi: 10.1016/j.edumed.2017.03.001 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources