Maternal Infection with Listeria monocytogenes in Twin Pregnancy
- PMID: 37138841
- PMCID: PMC10150742
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S407244
Maternal Infection with Listeria monocytogenes in Twin Pregnancy
Abstract
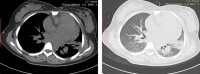
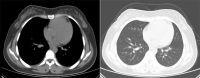
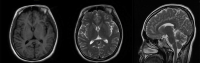
Listeria monocytogenes is the conditional pathogenic bacteria, and pregnant women are at higher risk of infection due to depressed immunity. Infection with Listeria monocytogenes in twin pregnancy is rare but devastating, which puts forwards a great challenge for clinical management. Here, a 24-year-old woman was diagnosed with twin pregnancy, intrauterine death of one fetus and fever at 29+4 week of gestation. Two days later, she developed into pericardial effusion, pneumonedema and potential septic shock. The emergent cesarean delivery was performed after anti-shock treatment. One alive and another dead fetus were delivered. Then, she developed postpartum hemorrhage after the surgery. Urgent exploratory laparotomy was conducted at the sites of cesarean section and B-Lynch suture to stop bleeding. The culture of blood and maternal side of both placentas indicated Listeria monocytogenes. Following anti-infection therapy with ampicillin-sulbactam, she recovered well and discharged with negative result of blood bacterial culture and normal inflammatory indicators. The patient was hospitalized for a total of 18 days including 2 days in the intensive care unit (ICU), and the anti-infection treatment was conducted throughout the course. Symptoms of the Listeria monocytogenes infection in pregnancy are non-specific, which should be paid more attention in case of unexplained fever and fetal distress. The blood culture is effective for accurate diagnosis. Listeria monocytogenes infection is associated with poor pregnancy outcomes. Close monitoring of fetal condition, early intervention with antibiotics, timely termination of pregnancy and comprehensive management of complications are essential for better prognosis.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; outcomes; twin pregnancy.
© 2023 Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Pengzhu Huang and Xin Guo contributed equally to this work as co-first authors. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Listeria monocytogenes bacteremia in a twin pregnancy with differential outcome: fetus papyraceus and a full-term delivery.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008 Oct;41(5):433-6. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008. PMID: 19122927
-
Neglected listeria infection in pregnancy in China: 93 cases.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Dec;35(25):9549-9557. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2022.2047925. Epub 2022 Mar 9. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 35264053
-
[Neonatal septicemia caused by Listeria monocytogenes: report of 6 cases].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Jan;46(1):22-5. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18353233 Chinese.
-
Successful treatment of maternal listeria monocytogenes bacteremia in the first trimester of pregnancy: A case report and literature review.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jun;57(3):462-463. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2018.04.025. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29880186 Review.
-
Delayed interval delivery of two remaining fetuses in quintuplet pregnancy after embryo reduction: report and review of the literature.Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma). 1992;41(1):49-52. doi: 10.1017/s0001566000002506. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma). 1992. PMID: 1488856 Review.
Cited by
-
Virulence Gene Profiling and Molecular Typing of Clinical Isolates of Listeria monocytogenes from Wenzhou, Eastern China.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Aug 8;18:3957-3966. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S526926. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40799954 Free PMC article.
-
Recurring food source-based Listeria outbreaks in the United States: An unsolved puzzle of concern?Health Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 4;7(2):e1863. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1863. eCollection 2024 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38317674 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

