High-fat diets enhance and delay ursodeoxycholic acid absorption but elevate circulating hydrophobic bile salts
- PMID: 37138846
- PMCID: PMC10149867
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1168144
High-fat diets enhance and delay ursodeoxycholic acid absorption but elevate circulating hydrophobic bile salts
Abstract
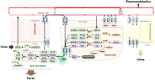
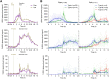
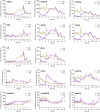
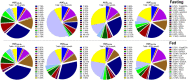
Background: Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a natural drug essential for the treatment of cholestatic liver diseases. The food effects on the absorption of UDCA and the disposition of circulating bile salts remain unclear despite its widespread global uses. This study aims to investigate the effects of high-fat (HF) diets on the pharmacokinetics of UDCA and disclose how the circulated bile salts were simultaneously perturbed. Methods: After an overnight fast, a cohort of 36 healthy subjects received a single oral dose (500 mg) of UDCA capsules, and another cohort of 31 healthy subjects received the same dose after consuming a 900 kcal HF meal. Blood samples were collected from 48 h pre-dose up to 72 h post-dose for pharmacokinetic assessment and bile acid profiling analysis. Results: The HF diets significantly delayed the absorption of UDCA, with the Tmax of UDCA and its major metabolite, glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA), changing from 3.3 h and 8.0 h in the fasting study to 4.5 h and 10.0 h in the fed study, respectively. The HF diets did not alter the Cmax of UDCA and GUDCA but immediately led to a sharp increase in the plasma levels of endogenous bile salts including those hydrophobic ones. The AUC0-72h of UDCA significantly increased from 25.4 μg h/mL in the fasting study to 30.8 μg h/mL in the fed study, while the AUC0-72h of GUDCA showed no difference in both studies. As a result, the Cmax of total UDCA (the sum of UDCA, GUDCA, and TUDCA) showed a significant elevation, while the AUC0-72h of total UDCA showed a slight increase without significance in the fed study compared to the fasting study. Conclusion: The HF diets delay UDCA absorption due to the extension of gastric empty time. Although UDCA absorption was slightly enhanced by the HF diets, the beneficial effect may be limited in consideration of the simultaneous elevation of circulating hydrophobic bile salts.
Keywords: bile acids; bile salts; food effect; glycoursodeoxycholic acid; pharmacokinetics; ursodeoxycholic acid.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Wei, Huang, Li, Liu, Gui, Jiang, Wan, Zhou, Ding, Jiang, Zhang and Lan.
Conflict of interest statement
Author XL, LG, JJ, LW, XZ, and KL were employed by Chengdu Cynogen Bio-pharmaceutical Tech. Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of common polymorphisms of the farnesoid X receptor and bile acid transporters on the pharmacokinetics of ursodeoxycholic acid.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Jan;43(1):34-40. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12490. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26382575 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of cholestyramine on bile acid pattern and synthesis during administration of ursodeoxycholic acid in man.Eur J Clin Invest. 2000 Feb;30(2):135-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2000.00606.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10651838
-
Intestinal absorption and biliary secretion of ursodeoxycholic acid and its taurine conjugate.Eur J Clin Invest. 2002 Aug;32(8):575-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2002.01030.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12190957 Clinical Trial.
-
Intestinal absorption of bile acids: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment.Ital J Gastroenterol. 1995 May;27(4):193-5. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1995. PMID: 8520037 Review.
-
Hepatocellular bile acid transport and ursodeoxycholic acid hypercholeresis.Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Dec;34(12 Suppl):5S-15S. doi: 10.1007/BF01536656. Dig Dis Sci. 1989. PMID: 2689116 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on Parkinson's disease, a mechanistic review of the recent evidence.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Feb 1;40(2):115. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01542-9. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39891787 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

