MicroRNA: role in macrophage polarization and the pathogenesis of the liver fibrosis
- PMID: 37138859
- PMCID: PMC10149999
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1147710
MicroRNA: role in macrophage polarization and the pathogenesis of the liver fibrosis
Abstract
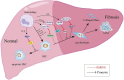
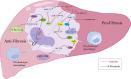
Macrophages, as central components of innate immunity, feature significant heterogeneity. Numerus studies have revealed the pivotal roles of macrophages in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis induced by various factors. Hepatic macrophages function to trigger inflammation in response to injury. They induce liver fibrosis by activating hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), and then inflammation and fibrosis are alleviated by the degradation of the extracellular matrix and release of anti-inflammatory cytokines. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small non-coding endogenous RNA molecules that regulate gene expression through translation repression or mRNA degradation, have distinct roles in modulating macrophage activation, polarization, tissue infiltration, and inflammation regression. Considering the complex etiology and pathogenesis of liver diseases, the role and mechanism of miRNAs and macrophages in liver fibrosis need to be further clarified. We first summarized the origin, phenotypes and functions of hepatic macrophages, then clarified the role of miRNAs in the polarization of macrophages. Finally, we comprehensively discussed the role of miRNAs and macrophages in the pathogenesis of liver fibrotic disease. Understanding the mechanism of hepatic macrophage heterogeneity in various types of liver fibrosis and the role of miRNAs on macrophage polarization provides a useful reference for further research on miRNA-mediated macrophage polarization in liver fibrosis, and also contributes to the development of new therapies targeting miRNA and macrophage subsets for liver fibrosis.
Keywords: HSC; M1 macrophage; M2 macrophage; liver fibrosis; macrophage polarization; microRNA.
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Wang, Wang, Chen, Nie, Liu, Zou, Gong and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of alternative polarization of macrophages by short-term activated hepatic stellate cell-derived small extracellular vesicles.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 10;44(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03380-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40211350 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Polarization and Its Role in Liver Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:803037. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.803037. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response.Shock. 2016 Aug;46(2):122-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000604. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26954942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miRNAs in macrophage-mediated kidney injury.Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Dec;39(12):3397-3410. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06414-5. Epub 2024 May 27. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38801452 Review.
-
Phillygenin inhibited M1 macrophage polarization and reduced hepatic stellate cell activation by inhibiting macrophage exosomal miR-125b-5p.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114264. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114264. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36652738
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Micro-RNAs in Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2025 Jun;45(2):167-179. doi: 10.1055/a-2494-2233. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Semin Liver Dis. 2025. PMID: 39626790 Review.
-
Regulation of immune cells by miR-451 and its potential as a biomarker in immune-related disorders: a mini review.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 15;15:1421473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421473. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39076992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-Based Therapy in Cardiovascular Diseases: A New Frontier in Cardiovascular Disease Treatment.Korean Circ J. 2025 Jun;55(6):461-480. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2025.0022. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Korean Circ J. 2025. PMID: 40206010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage polarization in spinal cord injury repair and the possible role of microRNAs: A review.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 27;9(12):e22914. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22914. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38125535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-27b-3p reduces muscle fibrosis during chronic skeletal muscle injury by targeting TGF-βR1/Smad pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jun 2;19(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04733-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38825706 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical