Prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 37138876
- PMCID: PMC10149806
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1119168
Prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is highly expressed in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) tissues. But there is still a dispute over the prognostic value of PD-L1 in patients with ICC. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in patients with ICC.
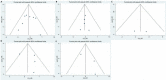
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Guidelines. We searched the literature from PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library up to December 5, 2022. Hazard ratios (HR) and their 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated to analyze the overall survival (OS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), and time to relapse. The quality of the studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. Publication bias was assessed using a funnel plot and Egger's test.
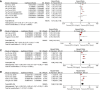
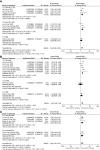
Results: Ten trials with 1944 cases were included in this meta-analysis. The results showed that the low-PD-L1 group had a statistically significant advantage in OS (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.38-1.79, P <0.00001), RFS (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.34-1.97, P <0.00001), and time to relapse (HR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.25-2.05, P = 0.0002) compared with the high-PD-L1 group. High programmed cell death (PD1)levels, on the other hand, were correlated with poorer OS (HR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.43-2.70; P <0.0001) and RFS (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.21-2.91; P = 0.005). Multivariate analysis showed that PD-L1 could act as an independent predictor for OS (HR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.14-1.91; P = 0.003) and RFS (HR, 1.74; 95% CI, 1.22-2.47; P = 0.002), and PD1 acted as an independent predictor for OS (HR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.15-2.38; P = 0.006).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis demonstrated that high PD-L1/PD1 expression is associated with poor survival in ICC. PD-L1/PD1 may be a valuable prognostic and predictive biomarker and potential therapeutic target in ICC.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42022380093.
Keywords: intrahepatic carcinoma; meta-analysis; prognostic value; programmed cell death 1 (PD-1); programmed cell death ligand 1 (PDL1).
Copyright © 2023 Xian, Ren, Bie and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CTLA-4 Synergizes With PD1/PD-L1 in the Inhibitory Tumor Microenvironment of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 30;12:705378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705378. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34526987 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand-1 expression in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical cystectomy: A meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 28;13:986911. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.986911. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36248912 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of PD-L1 expression in response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for biliary tract cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 28;15:1321813. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1321813. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38605964 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Is Associated with the Prognosis of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Feb;65(2):480-488. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05787-0. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31410753
-
Prognostic significance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression on circulating tumor cells in various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2021 Oct;10(20):7021-7039. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4236. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34423578 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tumor immune microenvironment and the current immunotherapy of cholangiocarcinoma (Review).Int J Oncol. 2023 Dec;63(6):137. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5585. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37888583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor combined with other targeted or immunological therapy regimens for the treatment of advanced bile tract cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 May 22;15:1378760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378760. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38840927 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

