Discrepancies of video head impulse test results in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo and vestibular neuritis
- PMID: 37139518
- PMCID: PMC10150120
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1102512
Discrepancies of video head impulse test results in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo and vestibular neuritis
Abstract
Objective: Sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo (SHLV) and vestibular neuritis (VN) remain frequent causes of acute vestibular syndrome (AVS). The aim of study was to compare the results of video head impulse test (vHIT) in patients with SHLV and VN. The characteristics of high-frequency vestibule-ocular reflex (VOR) and the differences of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying these two AVS were explored.
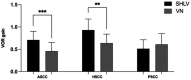
Methods: Fifty-seven SHLV patients and 31 VN patients were enrolled. vHIT was conducted at the initial presentation. The VOR gains and occurrence of corrective saccades (CSs) of anterior, horizontal, and posterior semicircular canals (SCCs) in two groups were analyzed. Pathological vHIT results refer to impaired VOR gains and presence of CSs.
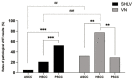
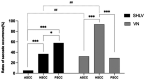
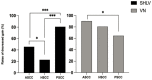
Results: In SHLV group, pathological vHIT results was most prevalent in the posterior SCC on the affected side (30/57, 52.63%), followed by horizontal (12/57, 21.05%) and anterior SCC (3/57, 5.26%). In VN group, pathological vHIT preferentially affected horizontal SCC (24/31, 77.42%), followed by anterior (10/31, 32.26%) and posterior SCC (9/31, 29.03%) on the affected side. As for anterior and horizontal SCC on the affected side, the incidences of pathological vHIT results in VN group were significantly higher than those in SHLV group (β = 2.905, p < 0.01; β = 2.183, p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in the incidence of pathological vHIT result in posterior SCC between two groups.
Conclusion: Comparison of vHIT results in patients with SHLV and VN revealed discrepancies in the pattern of SCCs impairments, which may be explained by different pathophysiological mechanisms underlying these two vestibular disorders presenting as AVS.
Keywords: gain; idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo; saccade; vestibular neuritis; vestibulo-ocular reflex; video head impulse test.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Leng, Zhou, Liu, Wang, Xia, Liu and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of vHIT deficits with Ramsay Hunt syndrome with dizziness, vestibular neuritis, and idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo.J Vestib Res. 2025 May;35(3):121-131. doi: 10.1177/09574271251313801. Epub 2025 Jan 15. J Vestib Res. 2025. PMID: 39973591
-
Differences in semicircular canal function in the video head impulse test in patients in the chronic stage of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo and vestibular neuritis.Acta Otolaryngol. 2024 Feb;144(2):123-129. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2024.2330680. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Acta Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38546396
-
Characteristics of spontaneous nystagmus and its correlation to video head impulse test findings in vestibular neuritis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 22;17:1243720. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1243720. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37674516 Free PMC article.
-
VOR gain of lateral semicircular canal using video head impulse test in acute unilateral vestibular hypofunction: A systematic review.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 8;13:948462. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.948462. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36570452 Free PMC article.
-
Video head impulse test: a review of the literature.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1215-1222. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4157-4. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27328962 Review.
Cited by
-
Normal horizontal VOR gain and catch-up saccades: still a diagnostic dilemma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09490-x. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40439923
-
Neurotologic Findings of Idiopathic Acute Unilateral Audiovestibulopathy.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Jul;32(7):e70278. doi: 10.1111/ene.70278. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40631769 Free PMC article.
-
Bilaterally positive head-impulse tests can differentiate AICA infarction from labyrinthitis.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1448989. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1448989. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39268064 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional characteristics of nystagmus induced by low frequency in semicircular canals of healthy young people.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jan 4;17:1321906. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1321906. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38239831 Free PMC article.
-
Video Head Impulse Test Coherence Predicts Vertigo Recovery in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss With Vertigo.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Nov;17(4):282-291. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2024.00068. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39501570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castellucci A., Pepponi E., Bertellini A., Senesi C., Bettini M., Botti C., et al. . (2020). Case report: filling defect in posterior Semicircular Canal on MRI with balanced steady-state gradient-Echo sequences after labyrinthine ischemia in the common Cochlear artery territory as an early sign of fibrosis. Front. Neurol. 11:608838. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.608838, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

