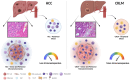
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor microenvironment is more suppressive than colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 37142825
- PMCID: PMC11014815
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10537-6
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor microenvironment is more suppressive than colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) tumor microenvironment
Abstract
Background and purpose: While HCC is an inflammation-associated cancer, CRLM develops on permissive healthy liver microenvironment. To evaluate the immune aspects of these two different environments, peripheral blood-(PB), peritumoral-(PT) and tumoral tissues-(TT) from HCC and CRLM patients were evaluated.
Methods: 40 HCC and 34 CRLM were enrolled and freshly TT, PT and PB were collected at the surgery. PB-, PT- and TT-derived CD4+CD25+ Tregs, M/PMN-MDSC and PB-derived CD4+CD25- T-effector cells (Teffs) were isolated and characterized. Tregs' function was also evaluated in the presence of the CXCR4 inhibitor, peptide-R29, AMD3100 or anti-PD1. RNA was extracted from PB/PT/TT tissues and tested for FOXP3, CXCL12, CXCR4, CCL5, IL-15, CXCL5, Arg-1, N-cad, Vim, CXCL8, TGFβ and VEGF-A expression.
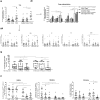
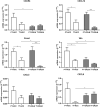
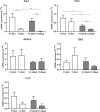
Results: In HCC/CRLM-PB, higher number of functional Tregs, CD4+CD25hiFOXP3+ was detected, although PB-HCC Tregs exert a more suppressive function as compared to CRLM Tregs. In HCC/CRLM-TT, Tregs were highly represented with activated/ENTPD-1+Tregs prevalent in HCC. As compared to CRLM, HCC overexpressed CXCR4 and N-cadherin/vimentin in a contest rich in arginase and CCL5. Monocytic MDSCs were highly represented in HCC/CRLM, while high polymorphonuclear MDSCs were detected only in HCC. Interestingly, the function of CXCR4-PB-Tregs was impaired in HCC/CRLM by the CXCR4 inhibitor R29.
Conclusion: In HCC and CRLM, peripheral blood, peritumoral and tumoral tissues Tregs are highly represented and functional. Nevertheless, HCC displays a more immunosuppressive TME due to Tregs, MDSCs, intrinsic tumor features (CXCR4, CCL5, arginase) and the contest in which it develops. As CXCR4 is overexpressed in HCC/CRLM tumor/TME cells, CXCR4 inhibitors may be considered for double hit therapy in liver cancer patients.
Keywords: CXCR4; CXCR4 inhibitors; ENTPD1; Immune cells and the microenvironment; Inflammation-associated cancer; Liver cancer; Liver metastases; Liver microenvironment; Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; Regulatory T cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The authors Sara Santagata, Giuseppina Rea, Daniela Castaldo, Maria Napolitano, Anna Capiluongo, Crescenzo D’Alterio, Anna Maria Trotta, Caterina Ieranò, Luigi Portella, Salvatore Di Maro, Fabiana Tatangelo,Vittorio Albino, Rita Guarino, Carmen Cutolo, Francesco Izzo, and Stefania Scala declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer C et al. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(12):1683–1691. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

