KMT2D Deficiency Promotes Myeloid Leukemias which Is Vulnerable to Ribosome Biogenesis Inhibition
- PMID: 37142882
- PMCID: PMC10323629
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202206098
KMT2D Deficiency Promotes Myeloid Leukemias which Is Vulnerable to Ribosome Biogenesis Inhibition
Abstract
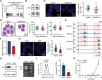
KMT2C and KMT2D are the most frequently mutated epigenetic genes in human cancers. While KMT2C is identified as a tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the role of KMT2D remains unclear in this disease, though its loss promotes B cell lymphoma and various solid cancers. Here, it is reported that KMT2D is downregulated or mutated in AML and its deficiency, through shRNA knockdown or CRISPR/Cas9 editing, accelerates leukemogenesis in mice. Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and AML cells with Kmt2d loss have significantly enhanced ribosome biogenesis and consistently, enlarged nucleolus, increased rRNA and protein synthesis rates. Mechanistically, it is found that KMT2D deficiency leads to the activation of the mTOR pathway in both mouse and human AML cells. Kmt2d directly regulates the expression of Ddit4, a negative regulator of the mTOR pathway. Consistent with the abnormal ribosome biogenesis, it is shown that CX-5461, an inhibitor of RNA polymerase I, significantly restrains the growth of AML with Kmt2d loss in vivo and extends the survival of leukemic mice. These studies validate KMT2D as a de facto tumor suppressor in AML and reveal an unprecedented vulnerability to ribosome biogenesis inhibition.
Keywords: KMT2D; acute myeloid leukemia; epigenetics; mTOR; ribosome biogenesis.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82130007/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022M722272/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2018RZ0140/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2022SCUH0037/"From 0 to 1" Innovation Project of Sichuan University
- 19HXFH030/Incubation Program for Clinical Trials, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- ZYJC21007/1.3.5 Project for Disciplines of Excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- ZYJC21009/1.3.5 Project for Disciplines of Excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- ZYGD22012/1.3.5 Project for Disciplines of Excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- National Institute of Health Research Biomedical Research Centre
- 2023HXBH019/Post-Doctor Research Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University
- 2023SCU12073/Post-Doctor Research Project of Sichuan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
