Elimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms on titanium implants via photothermally-triggered nitric oxide and immunotherapy for enhanced osseointegration
- PMID: 37143145
- PMCID: PMC10158155
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-023-00454-y
Elimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms on titanium implants via photothermally-triggered nitric oxide and immunotherapy for enhanced osseointegration
Abstract
Background: Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) biofilm infections in implant placement surgery is limited by the lack of antimicrobial activity of titanium (Ti) implants. There is a need to explore more effective approaches for the treatment of MRSA biofilm infections.
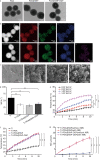
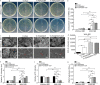
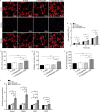
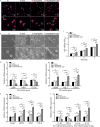
Methods: Herein, an interfacial functionalization strategy is proposed by the integration of mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles (PDA), nitric oxide (NO) release donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and osteogenic growth peptide (OGP) onto Ti implants, denoted as Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP. The physical and chemical properties of Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP were assessed by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscope, water contact angle, photothermal property and NO release behavior. The synergistic antibacterial effect and elimination of the MRSA biofilms were evaluated by 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate probe, 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine assay, adenosine triphosphate intensity, o-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside hydrolysis activity, bicinchoninic acid leakage. Fluorescence staining, assays for alkaline phosphatase activity, collagen secretion and extracellular matrix mineralization, quantitative real‑time reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were used to evaluate the inflammatory response and osteogenic ability in bone marrow stromal cells (MSCs), RAW264.7 cells and their co-culture system. Giemsa staining, ELISA, micro-CT, hematoxylin and eosin, Masson's trichrome and immunohistochemistry staining were used to evaluate the eradication of MRSA biofilms, inhibition of inflammatory response, and promotion of osseointegration of Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP in vivo.
Results: Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP displayed a synergistic photothermal and NO-dependent antibacterial effect against MRSA following near-infrared light irradiation, and effectively eliminated the formed MRSA biofilms by inducing reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated oxidative stress, destroying bacterial membrane integrity and causing leakage of intracellular components (P < 0.01). In vitro experiments revealed that Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP not only facilitated osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, but also promoted the polarization of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages to the anti-inflammatory M2-phenotype (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The favorable osteo-immune microenvironment further facilitated osteogenesis of MSCs and the anti-inflammation of RAW264.7 cells via multiple paracrine signaling pathways (P < 0.01). In vivo evaluation confirmed the aforementioned results and revealed that Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP induced ameliorative osseointegration in an MRSA-infected femoral defect implantation model (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP is a promising multi-functional material for the high-efficient treatment of MRSA infections in implant replacement surgeries.
Keywords: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Nitric oxide; Osseointegration; Osteo-immunomodulation; Photothermal effect; Polydopamine nanoparticles; Titanium implants.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yang J, Wang C, Liu X, Yin Y, Ma YH, Gao Y, et al. Gallium-carbenicillin framework coated defect-rich hollow TiO2 as a photocatalyzed oxidative stress amplifier against complex infections. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(43):2004861. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202004861. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

