miR-22 gene therapy treats HCC by promoting anti-tumor immunity and enhancing metabolism
- PMID: 37143325
- PMCID: PMC10277895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.04.019
miR-22 gene therapy treats HCC by promoting anti-tumor immunity and enhancing metabolism
Abstract
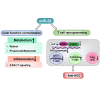
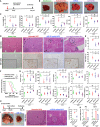
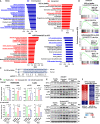
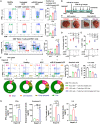
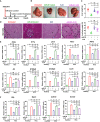
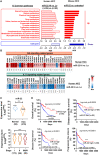
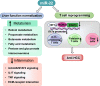
MicroRNA-22 (miR-22) can be induced by beneficial metabolites that have metabolic and immune effects, including retinoic acids, bile acids, vitamin D3, and short-chain fatty acids. The tumor suppressor effects of miR-22 have been suggested, but whether miR-22 treats orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is not established. The role of miR-22 in regulating tumor immunity is also poorly understood. Our data showed that miR-22 delivered by adeno-associated virus serotype 8 effectively treated HCC. Compared with FDA-approved lenvatinib, miR-22 produced better survival outcomes without noticeable toxicity. miR-22 silenced hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1α) and enhanced retinoic acid signaling in both hepatocytes and T cells. Moreover, miR-22 treatment improved metabolism and reduced inflammation. In the liver, miR-22 reduced the abundance of IL17-producing T cells and inhibited IL17 signaling by reducing the occupancy of HIF1α in the Rorc and Il17a genes. Conversely, increasing IL17 signaling ameliorated the anti-HCC effect of miR-22. Additionally, miR-22 expanded cytotoxic T cells and reduced regulatory T cells (Treg). Moreover, depleting cytotoxic T cells also abolished the anti-HCC effects of miR-22. In patients, miR-22 high HCC had upregulated metabolic pathways and reduced IL17 pro-inflammatory signaling compared with miR-22 low HCC. Together, miR-22 gene therapy can be a novel option for HCC treatment.
Keywords: HIF1α; RORγ; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; liver cancer; retinoic acid; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-342-3p is a potent tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2021 Jan;74(1):122-134. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.039. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 32738449
-
MicroRNA-639 is Down-Regulated in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumor Tissue and Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Through the KAT7/Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jan 19;26:e919241. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919241. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 31955177 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Tumor Suppressor MiR-34a Loaded on ZSM-5 Nanozeolite in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approach.Curr Gene Ther. 2019;19(5):342-354. doi: 10.2174/1566523219666191108103739. Curr Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 31701846
-
Underexpressed microRNA-199b-5p targets hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Nov;26(11):1630-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06758.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21557766
-
MicroRNA-503 inhibits the G1/S transition by downregulating cyclin D3 and E2F3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2013 Aug 22;11:195. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-195. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23967867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiRNAs in Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward New Therapeutic Approaches?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;15(23):5557. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235557. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of tetrahedral framework nucleic acids and tFNAs-miR22 on retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury.Cell Prolif. 2024 Nov;57(11):e13695. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13695. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 39086110 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and mechanisms of coding and noncoding RNA variations in cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Sep;56(9):1909-1920. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01307-x. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39218979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-22/GLUT1 Axis Induces Metabolic Reprogramming and Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3808. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083808. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332478 Free PMC article.
-
The role of viral infection in implantation failure: direct and indirect effects.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Nov 11;22(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01303-w. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39529140 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

