A simple fruit and vegetable score is a valid tool to assess actual fruit and vegetable intake
- PMID: 37143365
- PMCID: PMC10632721
- DOI: 10.1017/S0007114523001125
A simple fruit and vegetable score is a valid tool to assess actual fruit and vegetable intake
Abstract
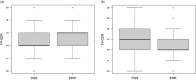
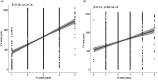
With the recent growing interest in improving fruit and vegetable intake for better health and limited research resources in many settings, simple-to-administer and low-priced indicators are essential tools for monitoring fruit and vegetable intake at the population level. A potential candidate indicator is the fruit and vegetable component of the Global Dietary Recommendation score (FV-GDR) based on data collected using the Diet Quality Questionnaire (DQQ). We investigated the relative validity of FV-GDR collected with the DQQ to measure fruit and vegetable intake by comparison with a 24-h recall (24hR) as a reference collected from 620 Vietnamese and 630 Nigerian adults in 2021. We found proportional differences in the prevalence of intake of vitamin A-rich vegetables, other vegetables and other fruits in Vietnam and all vegetable food groups in Nigeria. In both countries, we found a small difference in the total FV-GDR from DQQ compared with the 24hR, and the percentage of agreement between the two methods was quite high for the majority of the food groups. The FV-GDR calculated from the DQQ correlated with the actual intake, although less strongly than the FV-GDR from 24hR. The DQQ is a promising low-burden, low-cost and simple tool to calculate FV-GDR and to monitor fruit and vegetable consumption at the population level. This provides the possibility of evaluating an important aspect of diet quality in low-resource settings.
Keywords: Consumption; Diet quality; Dietary assessment; Food groups; Fruit and vegetable component of the Global Dietary Recommendation score; Indicator; Validation.
Figures

References
-
- Jayawardena R, Jeyakumar DT, Gamage M, et al. (2020) Fruit and vegetable consumption among South Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr (Internet) 14, 1791–1800. - PubMed
-
- Mensah DO, Nunes AR, Bockarie T, et al. (2021) Meat, fruit, and vegetable consumption in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Nutr Rev (Internet) 79, 651–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

