Complete variable domain sequences of monoclonal antibody light chains identified from untargeted RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 37143670
- PMCID: PMC10151772
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1167235
Complete variable domain sequences of monoclonal antibody light chains identified from untargeted RNA sequencing data
Abstract
Introduction: Monoclonal antibody light chain proteins secreted by clonal plasma cells cause tissue damage due to amyloid deposition and other mechanisms. The unique protein sequence associated with each case contributes to the diversity of clinical features observed in patients. Extensive work has characterized many light chains associated with multiple myeloma, light chain amyloidosis and other disorders, which we have collected in the publicly accessible database, AL-Base. However, light chain sequence diversity makes it difficult to determine the contribution of specific amino acid changes to pathology. Sequences of light chains associated with multiple myeloma provide a useful comparison to study mechanisms of light chain aggregation, but relatively few monoclonal sequences have been determined. Therefore, we sought to identify complete light chain sequences from existing high throughput sequencing data.
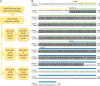
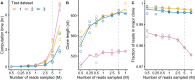
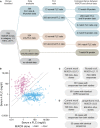
Methods: We developed a computational approach using the MiXCR suite of tools to extract complete rearranged IGVL-IGJL sequences from untargeted RNA sequencing data. This method was applied to whole-transcriptome RNA sequencing data from 766 newly diagnosed patients in the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation CoMMpass study.
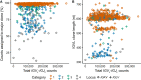
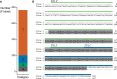
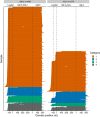
Results: Monoclonal IGVL-IGJL sequences were defined as those where >50% of assigned IGK or IGL reads from each sample mapped to a unique sequence. Clonal light chain sequences were identified in 705/766 samples from the CoMMpass study. Of these, 685 sequences covered the complete IGVL-IGJL region. The identity of the assigned sequences is consistent with their associated clinical data and with partial sequences previously determined from the same cohort of samples. Sequences have been deposited in AL-Base.
Discussion: Our method allows routine identification of clonal antibody sequences from RNA sequencing data collected for gene expression studies. The sequences identified represent, to our knowledge, the largest collection of multiple myeloma-associated light chains reported to date. This work substantially increases the number of monoclonal light chains known to be associated with non-amyloid plasma cell disorders and will facilitate studies of light chain pathology.
Keywords: AL amyloidosis; MiXCR; antibody light chain; antibody repertoire sequencing; antibody sequence; monoclonal gammopathy; multiple myeloma; plasma cell dyscrasia.
Copyright © 2023 Nau, Shen, Sanchorawala, Prokaeva and Morgan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of the mechanisms for antibody repertoire diversification in monoclonal light chain deposition disorders: when a friend becomes foe.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 13;14:1203425. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1203425. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An updated AL-Base reveals ranked enrichment of immunoglobulin light chain variable genes in AL amyloidosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 15:2024.09.11.612490. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612490. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Amyloid. 2025 Jun;32(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2024.2434899. PMID: 39314448 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
An updated AL-base reveals ranked enrichment of immunoglobulin light chain variable genes in AL amyloidosis.Amyloid. 2025 Jun;32(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2024.2434899. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Amyloid. 2025. PMID: 39641756
-
Mutations in specific structural regions of immunoglobulin light chains are associated with free light chain levels in patients with AL amyloidosis.PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005169. Epub 2009 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19365555 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and diversification of light chains in myeloma: the specter of amyloidogenesis by proxy.Contrib Nephrol. 2007;153:156-81. doi: 10.1159/000096766. Contrib Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17075229 Review.
Cited by
-
SMaRT M-Seq: an optimized step-by-step protocol for M protein sequencing in monoclonal gammopathies.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 Oct 3;9(1):bpae074. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae074. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39474207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the mechanisms for antibody repertoire diversification in monoclonal light chain deposition disorders: when a friend becomes foe.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 13;14:1203425. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1203425. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An updated AL-Base reveals ranked enrichment of immunoglobulin light chain variable genes in AL amyloidosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 15:2024.09.11.612490. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612490. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Amyloid. 2025 Jun;32(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2024.2434899. PMID: 39314448 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The smallest functional antibody fragment: Ultralong CDR H3 antibody knob regions potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Sep 26;120(39):e2303455120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2303455120. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37722054 Free PMC article.
-
An updated AL-base reveals ranked enrichment of immunoglobulin light chain variable genes in AL amyloidosis.Amyloid. 2025 Jun;32(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2024.2434899. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Amyloid. 2025. PMID: 39641756
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

