Reduced acetylated α-tubulin in SPAST hereditary spastic paraplegia patient PBMCs
- PMID: 37144097
- PMCID: PMC10152469
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1073516
Reduced acetylated α-tubulin in SPAST hereditary spastic paraplegia patient PBMCs
Abstract
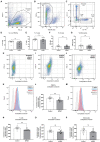
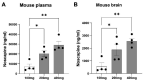
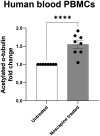
HSP-SPAST is the most common form of hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP), a neurodegenerative disease causing lower limb spasticity. Previous studies using HSP-SPAST patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell cortical neurons have shown that patient neurons have reduced levels of acetylated α-tubulin, a form of stabilized microtubules, leading to a chain of downstream effects eventuating in increased vulnerability to axonal degeneration. Noscapine treatment rescued these downstream effects by restoring the levels of acetylated α-tubulin in patient neurons. Here we show that HSP-SPAST patient non-neuronal cells, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), also have the disease-associated effect of reduced levels of acetylated α-tubulin. Evaluation of multiple PBMC subtypes showed that patient T cell lymphocytes had reduced levels of acetylated α-tubulin. T cells make up to 80% of all PBMCs and likely contributed to the effect of reduced acetylated α-tubulin levels seen in overall PBMCs. We further showed that mouse administered orally with increasing concentrations of noscapine exhibited a dose-dependent increase of noscapine levels and acetylated α-tubulin in the brain. A similar effect of noscapine treatment is anticipated in HSP-SPAST patients. To measure acetylated α-tubulin levels, we used a homogeneous time resolved fluorescence technology-based assay. This assay was sensitive to noscapine-induced changes in acetylated α-tubulin levels in multiple sample types. The assay is high throughput and uses nano-molar protein concentrations, making it an ideal assay for evaluation of noscapine-induced changes in acetylated α-tubulin levels. This study shows that HSP-SPAST patient PBMCs exhibit disease-associated effects. This finding can help expedite the drug discovery and testing process.
Keywords: biomarkers; hereditary spastic paraplegia; microtubule; neurodegenerative disease; noscapine.
Copyright © 2023 Wali, Siow, Liyanage, Kumar, Mackay-Sim and Sue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Benkert P., Meier S., Schaedelin S., Manouchehrinia A., Yaldizli Ö., Maceski A., et al. (2022). Serum neurofilament light chain for individual prognostication of disease activity in people with multiple sclerosis: a retrospective modelling and validation study. Lancet Neurol 21, 246–257. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00009-6, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

