Human pluripotent-stem-cell-derived organoids for drug discovery and evaluation
- PMID: 37146581
- PMCID: PMC10775018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.04.011
Human pluripotent-stem-cell-derived organoids for drug discovery and evaluation
Abstract
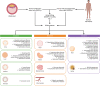
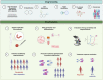
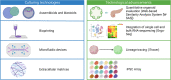
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) and three-dimensional organoids have ushered in a new era for disease modeling and drug discovery. Over the past decade, significant progress has been in deriving functional organoids from hPSCs, which have been applied to recapitulate disease phenotypes. In addition, these advancements have extended the application of hPSCs and organoids for drug screening and clinical-trial safety evaluations. This review provides an overview of the achievements and challenges in using hPSC-derived organoids to conduct relevant high-throughput, high-contentscreens and drug evaluation. These studies have greatly enhanced our knowledge and toolbox for precision medicine.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.C. is the co-founders of OncoBeat, LLC. S.C. is a consultant of Vesalius Therapeutics. S.C is a member of the advisory board of Cell Stem Cell.
Figures
References
-
- Marsee A., Roos F.J.M., Verstegen M.M.A., HPB Organoid Consortium. Gehart H., de Koning E., Lemaigre F., Forbes S.J., Peng W.C., Huch M., et al. Building consensus on definition and nomenclature of hepatic, pancreatic, and biliary organoids. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:816–832. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.04.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous