Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP) 1B3 is a Significant Transporter for Hepatic Uptake of Conjugated Bile Acids in Humans
- PMID: 37146714
- PMCID: PMC10394288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.04.007
Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP) 1B3 is a Significant Transporter for Hepatic Uptake of Conjugated Bile Acids in Humans
Abstract
Background & aims: OATP1B3/SLCO1B3 is a human liver-specific transporter for the clearance of endogenous compounds (eg, bile acid [BA]) and xenobiotics. The functional role of OATP1B3 in humans has not been characterized, as SLCO1B3 is poorly conserved among species without mouse orthologs.
Methods: Slc10a1-knockout (Slc10a1-/-), Slc10a1hSLCO1B3 (endogenous mouse Slc10a1 promoter-driven human-SLCO1B3 expression in Slc10a1-/- mice), and human SLCO1B3 liver-specific transgenic (hSLCO1B3-LTG) mice were generated and challenged with 0.1% ursodeoxycholic-acid (UDCA), 1% cholic-acid (CA) diet, or bile duct ligation (BDL) for functional studies. Primary hepatocytes and hepatoma-PLC/RPF/5 cells were used for mechanistic studies.
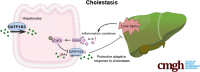
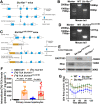
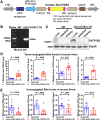
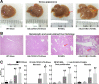
Results: Serum BA levels in Slc10a1-/- mice were substantially increased with or without 0.1% UDCA feeding compared with wild-type (WT) mice. This increase was attenuated in Slc10a1hSLCO1B3-mice, indicating that OATP1B3 functions as a significant hepatic BA uptake transporter. In vitro assay using primary hepatocytes from WT, Slc10a1-/-, and Slc10a1hSLCO1B3-mice indicated that OATP1B3 has a similar capacity in taking up taurocholate/TCA as Ntcp. Furthermore, TCA-induced bile flow was significantly impaired in Slc10a1-/- mice but partially recovered in Slc10a1hSLC01B3-mice, indicating that OATP1B3 can partially compensate the NTCP function in vivo. Liver-specific overexpression of OATP1B3 markedly increased the level of hepatic conjugated BA and cholestatic liver injury in 1% CA-fed and BDL mice. Mechanistic studies revealed that conjugated BAs stimulated Ccl2 and Cxcl2 in hepatocytes to increase hepatic neutrophil infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine production (eg, IL-6), which activated STAT3 to repress OATP1B3 expression by binding to its promoter.
Conclusions: Human OATP1B3 is a significant BA uptake transporter and can partially compensate Ntcp for conjugated BA uptake in mice. Its downregulation in cholestasis is an adaptive protective response.
Keywords: Bile Acid Transporter; Cholestasis; OATP1B3; Proinflammatory Cytokine.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Bile Salts by the Back Road.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;16(2):319-320. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.05.005. Epub 2023 May 24. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37244292 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wagner M., Zollner G., Trauner M. New molecular insights into the mechanisms of cholestasis. J Hepatol. 2009;51:565–580. - PubMed
-
- Arias I.M., Alter H.J., Boyer J.L., et al. Adaptive Regulation of Hepatocyte Transporters in Cholestasis. Fifth Edition. Wiley; 2009. The liver: biology and pathobiology; pp. 681–703.
-
- Jung D., Podvinec M., Meyer U.A., et al. Human organic anion transporting polypeptide 8 promoter is transactivated by the farnesoid X receptor/bile acid receptor. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1954–1966. - PubMed
-
- Durmus S., van Hoppe S., Schinkel A. The impact of organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATPs) on disposition and toxicity of antitumor drugs: insights from knockout and humanized mice. Drug Resist Updat. 2016;27:72–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

