Autoantibodies identify primary Sjögren's syndrome in patients lacking serum IgG specific for Ro/SS-A and La/SS-B
- PMID: 37147113
- PMCID: PMC10546962
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2022-223105
Autoantibodies identify primary Sjögren's syndrome in patients lacking serum IgG specific for Ro/SS-A and La/SS-B
Abstract
Objective: Identify autoantibodies in anti-Ro/SS-A negative primary Sjögren's syndrome (SS).
Methods: This is a proof-of-concept, case-control study of SS, healthy (HC) and other disease (OD) controls. A discovery dataset of plasma samples (n=30 SS, n=15 HC) was tested on human proteome arrays containing 19 500 proteins. A validation dataset of plasma and stimulated parotid saliva from additional SS cases (n=46 anti-Ro+, n=50 anti-Ro-), HC (n=42) and OD (n=54) was tested on custom arrays containing 74 proteins. For each protein, the mean+3 SD of the HC value defined the positivity threshold. Differences from HC were determined by Fisher's exact test and random forest machine learning using 2/3 of the validation dataset for training and 1/3 for testing. Applicability of the results was explored in an independent rheumatology practice cohort (n=38 Ro+, n=36 Ro-, n=10 HC). Relationships among antigens were explored using Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING) interactome analysis.
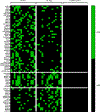
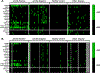
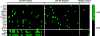
Results: Ro+ SS parotid saliva contained autoantibodies binding to Ro60, Ro52, La/SS-B and muscarinic receptor 5. SS plasma contained 12 novel autoantibody specificities, 11 of which were detected in both the discovery and validation datasets. Binding to ≥1 of the novel antigens identified 54% of Ro- SS and 37% of Ro+ SS cases, with 100% specificity in both groups. Machine learning identified 30 novel specificities showing receiver operating characteristic area under the curve of 0.79 (95% CI 0.64 to 0.93) for identifying Ro- SS. Sera from Ro- cases of an independent cohort bound 17 of the non-canonical antigens. Antigenic targets in both Ro+ and Ro- SS were part of leukaemia cell, ubiquitin conjugation and antiviral defence pathways.
Conclusion: We identified antigenic targets of the autoantibody response in SS that may be useful for identifying up to half of Ro seronegative SS cases.
Keywords: Sjogren's syndrome; autoantibodies; autoimmune diseases.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ADF and CJL have received grant support from Janssen Research and Development. AND has received consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Figures
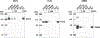


References
-
- Mariette X, Criswell LA. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2018. 2018–03-08; 378(10):931–939. - PubMed
-
- Shiboski CH, Shiboski SC, Seror R, Criswell LA, Labetoulle M, Lietman TM, et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjogren's Syndrome: A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017. Jan; 69(1):35–45. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

