Circulating tumor DNA reveals mechanisms of lorlatinib resistance in patients with relapsed/refractory ALK-driven neuroblastoma
- PMID: 37147298
- PMCID: PMC10163008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38195-0
Circulating tumor DNA reveals mechanisms of lorlatinib resistance in patients with relapsed/refractory ALK-driven neuroblastoma
Abstract
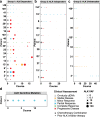
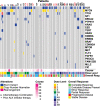
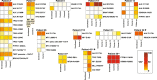
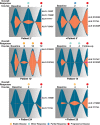
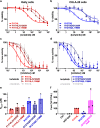
Activating point mutations in Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) have positioned ALK as the only mutated oncogene tractable for targeted therapy in neuroblastoma. Cells with these mutations respond to lorlatinib in pre-clinical studies, providing the rationale for a first-in-child Phase 1 trial (NCT03107988) in patients with ALK-driven neuroblastoma. To track evolutionary dynamics and heterogeneity of tumors, and to detect early emergence of lorlatinib resistance, we collected serial circulating tumor DNA samples from patients enrolled on this trial. Here we report the discovery of off-target resistance mutations in 11 patients (27%), predominantly in the RAS-MAPK pathway. We also identify newly acquired secondary compound ALK mutations in 6 (15%) patients, all acquired at disease progression. Functional cellular and biochemical assays and computational studies elucidate lorlatinib resistance mechanisms. Our results establish the clinical utility of serial circulating tumor DNA sampling to track response and progression and to discover acquired resistance mechanisms that can be leveraged to develop therapeutic strategies to overcome lorlatinib resistance.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.P.M. is the Principal Investigator of the NANT Phase 1 trial of lorlatinib and is a consultant for Pfizer. No research funding from Pfizer was received for this study. Y.P.M. has previously received research funding from Pfizer and Novartis. Y.P.M. has also served as a consultant for Lilly, Auron Therapeutics, and Jumo Health. Y.P.M. serves as a member of the Data and Safety Monitoring Committee for the ASCO TAPUR study and receives honoraria for this role. D.P. is an employee of Foundation Medicine. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

