Targeting long non-coding RNA NUDT6 enhances smooth muscle cell survival and limits vascular disease progression
- PMID: 37147804
- PMCID: PMC10277891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.04.020
Targeting long non-coding RNA NUDT6 enhances smooth muscle cell survival and limits vascular disease progression
Abstract
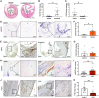
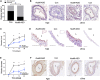
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) orchestrate various biological processes and regulate the development of cardiovascular diseases. Their potential therapeutic benefit to tackle disease progression has recently been extensively explored. Our study investigates the role of lncRNA Nudix Hydrolase 6 (NUDT6) and its antisense target fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) in two vascular pathologies: abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) and carotid artery disease. Using tissue samples from both diseases, we detected a substantial increase of NUDT6, whereas FGF2 was downregulated. Targeting Nudt6 in vivo with antisense oligonucleotides in three murine and one porcine animal model of carotid artery disease and AAA limited disease progression. Restoration of FGF2 upon Nudt6 knockdown improved vessel wall morphology and fibrous cap stability. Overexpression of NUDT6 in vitro impaired smooth muscle cell (SMC) migration, while limiting their proliferation and augmenting apoptosis. By employing RNA pulldown followed by mass spectrometry as well as RNA immunoprecipitation, we identified Cysteine and Glycine Rich Protein 1 (CSRP1) as another direct NUDT6 interaction partner, regulating cell motility and SMC differentiation. Overall, the present study identifies NUDT6 as a well-conserved antisense transcript of FGF2. NUDT6 silencing triggers SMC survival and migration and could serve as a novel RNA-based therapeutic strategy in vascular diseases.
Keywords: aortic aneurysm; atherosclerosis; long non-coding RNAs; proliferation; smooth muscle cell; therapeutics; vascular disease.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests L.M. is a scientific consultant and adviser for Novo Nordisk (Malov, Denmark), DrugFarm (Shanghai, China), and Angiolutions (Hannover, Germany), and received research funds from Roche Diagnostics (Rotkreuz, Switzerland) and Novo Nordisk (Malov, Denmark).
Figures





References
-
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

