An eosinophil peroxidase activity assay accurately predicts eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 37148919
- PMCID: PMC10524284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.04.012
An eosinophil peroxidase activity assay accurately predicts eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: A definitive diagnosis of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (eCRS) requires invasive surgical tissue sampling and histologic enumeration of intact eosinophils. Eosinophil peroxidase (EPX) is an accurate biomarker of sinonasal tissue eosinophilia in CRS regardless of polyp status. A less invasive and rapid method that accurately identifies tissue eosinophilia would be of great benefit to patients.
Objective: We sought to evaluate a new clinical tool that uses a nasal swab and colorimetric EPX activity assay to predict a diagnosis of eCRS.
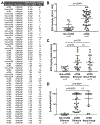
Methods: A prospective, observational cohort study was conducted using nasal swabs and sinonasal tissue biopsies obtained from patients with CRS electing endoscopic sinus surgery. Patients were classified as non-eCRS (n = 19) and eCRS (n = 35) on the basis of pathologically determined eosinophil counts of less than 10 or greater than or equal to 10 eosinophils/HPF, respectively. Swab-deposited EPX activity was measured and compared with tissue eosinophil counts, EPX levels, and CRS-specific disease metrics.
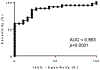
Results: EPX activity was significantly increased in patients with eCRS than in patients without eCRS (P < .0001). With a relative absorbance unit cutoff value of greater than or equal to 0.80, the assay demonstrated high sensitivity (85.7%) and moderate specificity (79.0%) for confirming eCRS. Spearman correlations between EPX activity and tissue eosinophil counts (rs = 0.424), EPX levels (rs = 0.503), and Lund-Kennedy endoscopy scores (rs = 0.440) in eCRS were significant (P < .05).
Conclusions: This investigation evaluates a nasal swab sampling method and EPX activity assay that accurately confirms eCRS. This method could potentially address the unmet need to identify sinonasal tissue eosinophilia at the point-of-care, as well as to longitudinally monitor eosinophil activity and treatment response.
Keywords: Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis; eosinophil peroxidase activity; ethmoid biopsy; nasal polyps; tissue eosinophilia.
Copyright © 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
In office sampling of eosinophil peroxidase to diagnose eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025 Jan;15(1):36-44. doi: 10.1002/alr.23448. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025. PMID: 39269218 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophil Peroxidase: A Biomarker for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis Agnostic of Polyp Status.Laryngoscope. 2024 Jan;134(1):69-78. doi: 10.1002/lary.30787. Epub 2023 May 31. Laryngoscope. 2024. PMID: 37255054 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis.Laryngoscope. 2004 Nov;114(11):1895-905. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000147917.43615.c0. Laryngoscope. 2004. PMID: 15510011
-
Systemic biomarkers of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Feb;20(1):23-29. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000602. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31688152 Review.
-
High tissue eosinophilia as a marker to predict recurrence for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018 Dec;8(12):1421-1429. doi: 10.1002/alr.22194. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018. PMID: 30091850
Cited by
-
Small proline-rich protein 2A drives epithelial remodeling in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps via SAA2 upregulation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 May 28:S0091-6749(25)00578-0. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.05.012. Online ahead of print. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40447198
-
The Influence of Allergic Biomarkers in Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients Who Underwent Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery.OTO Open. 2025 Jun 6;9(2):e70138. doi: 10.1002/oto2.70138. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2025. PMID: 40486977 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine CCL19 and Its Receptors CCR7 and CCRL1 in Chronic Rhinosinusitis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 May 14;17:2991-3002. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S453567. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38764495 Free PMC article.
-
In office sampling of eosinophil peroxidase to diagnose eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025 Jan;15(1):36-44. doi: 10.1002/alr.23448. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025. PMID: 39269218 Free PMC article.
-
Association between peripheral eosinophilia, JESREC score, and olfactory dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 24;15:1334656. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1334656. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38327522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeConde AS, Soler ZM. Chronic rhinosinusitis: Epidemiology and burden of disease. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016;30(2):134–9. - PubMed
-
- Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Smith TL, Bleier B, DeConde A, Luong AU, et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: rhinosinusitis 2021. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021;11(3):213–739. - PubMed
-
- Tomassen P, Vandeplas G, Van Zele T, Cardell LO, Arebro J, Olze H, et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137(5):1449–56 e4. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, et al. Executive summary of EPOS 2020 including integrated care pathways. Rhinology. 2020;58(2):82–111. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020;58(Suppl S29):1–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

