Mucinous appendix intussusception: Case report
- PMID: 37150162
- PMCID: PMC10192518
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108250
Mucinous appendix intussusception: Case report
Abstract
Introduction and importance: Intussusception is an intestinal invagination of one bowel segment into another. It occurs mostly in children, but it can show in adults due to different etiologies. Appendiceal neoplasms are rare and can mimic an acute onset of appendicitis. Appendiceal mucinous neoplasm is one of the subtypes of appendiceal malignancies found in less than 1 % of appendectomies samples.
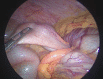
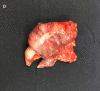
Case presentation: We present the case of a 32-year-old woman with abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant, whose computed tomography revealed an ileocolic intussusception and a low-density tubular image in the distal loop. She underwent diagnostic laparoscopy and laparoscopic right colectomy. Biopsy results confirmed a LAMN with acute appendicitis and intussusception.
Clinical discussion: Appendiceal intussusception (AI) is associated with the alteration of peristalsis, in addition to multiple inflammatory conditions and diseases such as parasites, foreign bodies, Crohn's disease, and lymphoid hyperplasia. The pathophysiology of AI is not fully established, but the main appendicular alteration that has been associated with it is the presence of a tumor. AI lead points are typically pathological in 90 % of cases, 65 % of which are neoplastic in nature. Right hemicolectomy should be performed for tumors involving the periappendicular area or in those larger than 2 cm in size. Follow-up and surveillance colonoscopy is suggested.
Conclusion: Intussusception is a rare diagnosis in adults. However, malignancy should be suspected if identified.
Keywords: Appendiceal mucinous neoplasm; Appendix; Case report; Intussusception.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Van de Moortele M., De Hertogh G., Sagaert X., Van Cutsem E. Appendiceal cancer : a review of the literature. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2020 Jul-Sep;83(3):441–448. PMID: 33094592. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

