Sustained Preservation of Cognition and Prevention of Patient-Reported Symptoms With Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: Final Results of NRG Oncology CC001
- PMID: 37150264
- PMCID: PMC11070071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.04.030
Sustained Preservation of Cognition and Prevention of Patient-Reported Symptoms With Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: Final Results of NRG Oncology CC001
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Gondi V, Deshmukh S, Brown PD, et al. Sustained Preservation of Cognition and Prevention of Patient-Reported Symptoms With Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: Final Results of NRG Oncology CC001. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023;117:571-580.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2025 Feb 1;121(2):571-572. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.08.041. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2025. PMID: 39824575 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Initial report of NRG Oncology CC001, a phase 3 trial of whole-brain radiation therapy plus memantine (WBRT + memantine) with or without hippocampal avoidance (HA), demonstrated neuroprotective effects of HA with a median follow-up of fewer than 8 months. Herein, we report the final results with complete cognition, patient-reported outcomes, and longer-term follow-up exceeding 1 year.
Methods and materials: Adult patients with brain metastases were randomized to HA-WBRT + memantine or WBRT + memantine. The primary endpoint was time to cognitive function failure, defined as decline using the reliable change index on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised (HVLT-R), Controlled Oral Word Association, or the Trail Making Tests (TMT) A and B. Patient-reported symptom burden was assessed using the MD Anderson Symptom Inventory with Brain Tumor Module and EQ-5D-5L.
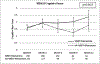
Results: Between July 2015 and March 2018, 518 patients were randomized. The median follow-up for living patients was 12.1 months. The addition of HA to WBRT + memantine prevented cognitive failure (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.74, P = .016) and was associated with less deterioration in TMT-B at 4 months (P = .012) and HVLT-R recognition at 4 (P = .055) and 6 months (P = .011). Longitudinal modeling of imputed data showed better preservation of all HVLT-R domains (P < .005). Patients who received HA-WBRT + Memantine reported less symptom burden at 6 (P < .001 using imputed data) and 12 months (P = .026 using complete-case data; P < .001 using imputed data), less symptom interference at 6 (P = .003 using complete-case data; P = .0016 using imputed data) and 12 months (P = .0027 using complete-case data; P = .0014 using imputed data), and fewer cognitive symptoms over time (P = .043 using imputed data). Treatment arms did not differ significantly in overall survival, intracranial progression-free survival, or toxicity.
Conclusions: With median follow-up exceeding 1 year, HA during WBRT + memantine for brain metastases leads to sustained preservation of cognitive function and continued prevention of patient-reported neurologic symptoms, symptom interference, and cognitive symptoms with no difference in survival or toxicity.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Monje ML, Mizumatsu S, Fike JR, et al. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat Med 2002;8:955–962. - PubMed
-
- Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, et al. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2013;85:348–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

