Research priorities for therapeutic plasma exchange in critically ill patients
- PMID: 37150798
- PMCID: PMC10164453
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-023-00510-w
Research priorities for therapeutic plasma exchange in critically ill patients
Abstract
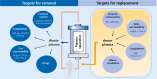
Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) is a therapeutic intervention that separates plasma from blood cells to remove pathological factors or to replenish deficient factors. The use of TPE is increasing over the last decades. However, despite a good theoretical rationale and biological plausibility for TPE as a therapy for numerous diseases or syndromes associated with critical illness, TPE in the intensive care unit (ICU) setting has not been studied extensively. A group of eighteen experts around the globe from different clinical backgrounds used a modified Delphi method to phrase key research questions related to "TPE in the critically ill patient". These questions focused on: (1) the pathophysiological role of the removal and replacement process, (2) optimal timing of treatment, (3) dosing and treatment regimes, (4) risk-benefit assumptions and (5) novel indications in need of exploration. For all five topics, the current understanding as well as gaps in knowledge and future directions were assessed. The content should stimulate future research in the field and novel clinical applications.
Keywords: Apheresis; Expert panel; Gaps; Knowledge; Plasma exchange; Plasmapheresis; Research.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SD has received research support and lecture honoraria from Terumo Blodd and Cell Technology, Octapharms and Bayer. JC received research funding from Cerus, Kawasumi Laboratories, Sanofi, Janssen, Incyte, and Sobi; he also received speaker or advisory fees from Cerus, Fresenius Kabi, Grifols, Macopharma, Pharm-Olam, Sanofi, and Terumo Blood and Cell Technologies. ACB received support from Octapharma for attending a meeting. PC has received honoraria for scientific collaboration with Pfizer, MSD and Gilead, and has participated in Advisory Boards for Alexion, Janssen and Gilead.
Figures
References
-
- Bauer PR, Ostermann M, Russell L, Robba C, David S, Ferreyro BL, Cid J, Castro P, Juffermans NP, Montini L, Pirani T, Van De Louw A, Nielsen N, Wendon J, Brignier AC, Schetz M, Kielstein JT, Winters JL, Azoulay E, Nine II. Plasma exchange in the intensive care unit: a narrative review. Intensive Care Med. 2022;48:1382–1396. doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06793-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coppo P, Schwarzinger M, Buffet M, Wynckel A, Clabault K, Presne C, Poullin P, Malot S, Vanhille P, Azoulay E, Galicier L, Lemiale V, Mira JP, Ridel C, Rondeau E, Pourrat J, Girault S, Bordessoule D, Saheb S, Ramakers M, Hamidou M, Vernant JP, Guidet B, Wolf M, Veyradier A, French Reference Center for Thrombotic M Predictive features of severe acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency in idiopathic thrombotic microangiopathies: the French TMA reference center experience. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e10208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010208. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, Russell L, Knoebl P, Martin-Loeches I, Pene F, Puxty K, Povoa P, Barratt-Due A, Garnacho-Montero J, Wendon J, Munshi L, Benoit D, von Bergwelt-Baildon M, Maggiorini M, Coppo P, Cataland S, Veyradier A, Van de Louw A, Nine-i I. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45:1518–1539. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Larsen FS, Schmidt LE, Bernsmeier C, Rasmussen A, Isoniemi H, Patel VC, Triantafyllou E, Bernal W, Auzinger G, Shawcross D, Eefsen M, Bjerring PN, Clemmesen JO, Hockerstedt K, Frederiksen HJ, Hansen BA, Antoniades CG, Wendon J. High-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure: an open randomised controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2016;64:69–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

