Bioinspired Dry Adhesives for Highly Adaptable and Stable Manipulating Irregular Objects under Vibration
- PMID: 37150863
- PMCID: PMC10375138
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202302512
Bioinspired Dry Adhesives for Highly Adaptable and Stable Manipulating Irregular Objects under Vibration
Abstract
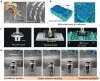
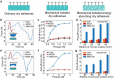
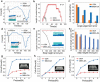
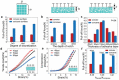
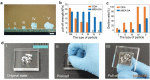
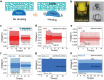
For dry adhesive-based operation, highly adaptable and stable manipulation is important but also challenging, especially for irregular objects with complex surface (such as abrupt profile and acute projection) under vibration-inducing environments. Here, a multi-scale adhesive structure, with mechanically isolated energy-absorbing backing, based on the synergistic action of microscale contact end (seta), mesoscale supporting layer (lamella), and macroscopic backing (muscle tissues) of gecko's sole, is proposed. Top layer of mushroom-like micro tips provides dry adhesion via mimicking gecko's seta, and bottom layer of physical cuts and porous feature achieves the interfacial mechanical decoupling and crack inhibition via mimicking the non-continuous distributing of lamella and compliance of muscle. The proposed dry adhesive exhibits excellent adaptable adhesion to various objects with curved or irregular surfaces, even for that with abrupt contours, as well as an amazing stable anti-vibration ability, opening a new avenue for the development of dry adhesive-based device or system.
Keywords: bioinspired adhesive materials; contact adaptability; irregular surfaces; multi-scale bionics; stable adhesion.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hao J., Hawkes E. W., Arutyunov V., Tims J., Cutkosky M. R., IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2015, 2015, 2828.
-
- Jiang H., Hawkes E. W., Fuller C., Estrada M. A., Cutkosky M. R., Sci. Rob. 2017, 2, eaan4545. - PubMed
-
- Dadkhah M., Zhao Z., Wettels N., Spenko M., in 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), IEEE, Piscataway, NJ: 2016, pp. 1006–1011.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
