Data-driven neuropathological staging and subtyping of TDP-43 proteinopathies
- PMID: 37150879
- PMCID: PMC10317181
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awad145
Data-driven neuropathological staging and subtyping of TDP-43 proteinopathies
Abstract
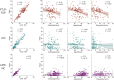
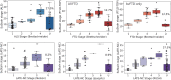
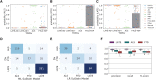
TAR DNA-binding protein-43 (TDP-43) accumulation is the primary pathology underlying several neurodegenerative diseases. Charting the progression and heterogeneity of TDP-43 accumulation is necessary to better characterize TDP-43 proteinopathies, but current TDP-43 staging systems are heuristic and assume each syndrome is homogeneous. Here, we use data-driven disease progression modelling to derive a fine-grained empirical staging system for the classification and differentiation of frontotemporal lobar degeneration due to TDP-43 (FTLD-TDP, n = 126), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, n = 141) and limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathologic change (LATE-NC) with and without Alzheimer's disease (n = 304). The data-driven staging of ALS and FTLD-TDP complement and extend previously described human-defined staging schema for ALS and behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia. In LATE-NC individuals, progression along data-driven stages was positively associated with age, but negatively associated with age in individuals with FTLD-TDP. Using only regional TDP-43 severity, our data driven model distinguished individuals diagnosed with ALS, FTLD-TDP or LATE-NC with a cross-validated accuracy of 85.9%, with misclassifications associated with mixed pathological diagnosis, age and genetic mutations. Adding age and SuStaIn stage to this model increased accuracy to 92.3%. Our model differentiates LATE-NC from FTLD-TDP, though some overlap was observed between late-stage LATE-NC and early-stage FTLD-TDP. We further tested for the presence of subtypes with distinct regional TDP-43 progression patterns within each diagnostic group, identifying two distinct cortical-predominant and brainstem-predominant subtypes within FTLD-TDP and a further two subcortical-predominant and corticolimbic-predominant subtypes within ALS. The FTLD-TDP subtypes exhibited differing proportions of TDP-43 type, while there was a trend for age differing between ALS subtypes. Interestingly, a negative relationship between age and SuStaIn stage was seen in the brainstem/subcortical-predominant subtype of each proteinopathy. No subtypes were observed for the LATE-NC group, despite aggregating individuals with and without Alzheimer's disease and a larger sample size for this group. Overall, we provide an empirical pathological TDP-43 staging system for ALS, FTLD-TDP and LATE-NC, which yielded accurate classification. We further demonstrate that there is substantial heterogeneity amongst ALS and FTLD-TDP progression patterns that warrants further investigation in larger cross-cohort studies.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; frontotemporal lobar degeneration; limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy; machine learning; neuropathological staging.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
O.H. has acquired research support (for the institution) from ADx, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Fujirebio, GE Healthcare, Pfizer and Roche. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from AC Immune, Amylyx, Alzpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Cerveau, Fujirebio, Genentech, Novartis, Roche and Siemens. L.E. receives consulting fees from Biogen, PTC Therapeutics, Apellis Pharmaceuticals and Edgewise Therapeutics. D.W. has served as a paid consultant to Eli Lilly, GE Healthcare and Qynapse. He serves on a DSMB for Functional Neuromodulation. He is a site investigator for a clinical trial sponsored by Biogen. R.O. has received research support from Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Janssen Research & Development, Roche, Quanterix and Optina Diagnostics, and has given lectures in symposia sponsored by GE Healthcare. He is an editorial board member of
Figures



Update of
-
Data-driven neuropathological staging and subtyping of TDP-43 proteinopathies.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 2:2023.01.31.23285242. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.31.23285242. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Brain. 2023 Jul 3;146(7):2975-2988. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad145. PMID: 36778217 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Precision diagnosis and staging of TDP-43 proteinopathies: harnessing the power of artificial intelligence.Brain. 2023 Jul 3;146(7):2666-2668. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad175. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37224516 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

