Detection and analysis of graduate students' academic emotions in the online academic forum based on text mining with a deep learning approach
- PMID: 37151331
- PMCID: PMC10157494
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1107080
Detection and analysis of graduate students' academic emotions in the online academic forum based on text mining with a deep learning approach
Abstract
Purpose: The possibility of mental illness caused by the academic emotions and academic pressure of graduate students has received widespread attention. Discovering hidden academic emotions by mining graduate students' speeches in social networks has strong practical significance for the mental state discovery of graduate students.
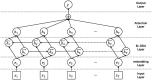
Design/methodology/approach: Through data collected from online academic forum, a text based BiGRU-Attention model was conducted to achieve academic emotion recognition and classification, and a keyword statistics and topic analysis was performed for topic discussion among graduate posts.
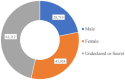
Findings: Female graduate students post more than male students, and graduates majoring in chemistry post the most. Using the BiGRU-Attention model to identify and classify academic emotions has a performance with precision, recall and F1 score of more than 95%, the category of PA (Positive Activating) has the best classification performance. Through the analysis of post topics and keywords, the academic emotions of graduates mainly come from academic pressure, interpersonal relationships and career related.
Originality: A BiGRU-Attention model based on deep learning method is proposed to combine classical academic emotion classification and categories to achieve a text academic emotion recognition method based on user generated content.
Keywords: academic emotion; deep learning; emotion classification; emotion recognition; graduate mental health.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Chen, Xu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Analysis of contemporary value and influence of intangible cultural heritage based on online review mining.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 19;19(12):e0315805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315805. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39700234 Free PMC article.
-
Academic Emotion Classification and Recognition Method for Large-scale Online Learning Environment-Based on A-CNN and LSTM-ATT Deep Learning Pipeline Method.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 16;17(6):1941. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17061941. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32188094 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Patient Sentiment and Emotion in Ophthalmology: Infoveillance Tutorial on Web-Based Health Forum Discussions.J Med Internet Res. 2021 May 17;23(5):e20803. doi: 10.2196/20803. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33999001 Free PMC article.
-
An open-source dataset for arabic fine-grained emotion recognition of online content amid COVID-19 pandemic.Data Brief. 2023 Oct 31;51:109745. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109745. eCollection 2023 Dec. Data Brief. 2023. PMID: 38020433 Free PMC article.
-
Exam Success at Undergraduate and Graduate-Entry Medical Schools: Is Learning Style or Learning Approach More Important? A Critical Review Exploring Links Between Academic Success, Learning Styles, and Learning Approaches Among School-Leaver Entry ("Traditional") and Graduate-Entry ("Nontraditional") Medical Students.Teach Learn Med. 2015;27(3):237-44. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2015.1046734. Teach Learn Med. 2015. PMID: 26158325 Review.
References
-
- Agrawal A., An A. (2012). Unsupervised emotion detection from text using semantic and syntactic relations. 2012 IEEE/WIC/ACM international conferences on web intelligence and intelligent agent technology, Melbourne, Australia 1, 346–353
-
- Ahmad Z., Jindal R., Ekbal A., Bhattachharyya P. (2020). Borrow from rich cousin: transfer learning for emotion detection using cross lingual embedding. Expert Syst. Appl. 139:112851. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112851 - DOI
-
- Ainley M., Corrigan M., Richardson N. (2005). Students, tasks and emotions: identifying the contribution of emotions to students' reading of popular culture and popular science texts. Learn. Instr. 15, 433–447. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2005.07.011 - DOI
-
- Are C., Stoddard H. A., Nelson K. L., Huggett K., Carpenter L., Thompson J. S. (2018). The influence of medical school on career choice: a longitudinal study of students’ attitudes toward a career in general surgery. Am. J. Surg. 216, 1215–1222. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2018.10.036, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asghar M. Z., Subhan F., Imran M., Kundi F. M., Shamshirband S., Mosavi A., et al. . (2019). Performance evaluation of supervised machine learning techniques for efficient detection of emotions from online content. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.01587. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1908.01587 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

