Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetases: Implications of Structural Biology in Drug Development against Trypanosomatid Parasites
- PMID: 37151504
- PMCID: PMC10157851
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00826
Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetases: Implications of Structural Biology in Drug Development against Trypanosomatid Parasites
Abstract
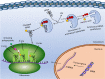
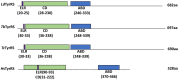
The ensemble of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases is regarded as a key component of the protein translation machinery. With the progressive increase in structure-based studies on tRNA synthetase-ligand complexes, the detailed picture of these enzymes is becoming clear. Having known their critical role in deciphering the genetic code in a living system, they have always been chosen as one of the important targets for development of antimicrobial drugs. Later on, the role of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) on the survivability of trypanosomatids has also been validated. It became evident through several gene knockout studies that targeting even one of these enzymes affected parasitic growth drastically. Such successful studies have inspired researchers to search for inhibitors that could specifically target trypanosomal aaRSs, and their never-ending efforts have provided fruitful results. Taking all such studies into consideration, these macromolecules of prime importance deserve further investigation for the development of drugs that cure spectrum of infections caused by trypanosomatids. In this review, we have compiled advancements of over a decade that have taken place in the pursuit of devising drugs by using trypanosomatid aaRSs as a major target of interest. Several of these inhibitors work on an exemplary low concentration range without posing any threat to the mammalian cells which is a very critical aspect of the drug discovery process. Advancements have been made in terms of using structural biology as an important tool to analyze the architecture of the trypanosomatids aaRSs and concoction of inhibitors with augmented specificities toward their targets. Some of the inhibitors that have been tested on other parasites successfully but their efficacy has so far not been validated against these trypanosomatids have also been appended.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Peculiarities of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases from trypanosomatids.J Biol Chem. 2021 Aug;297(2):100913. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100913. Epub 2021 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34175310 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights on trypanosomatid aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis.Subcell Biochem. 2014;74:271-304. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7305-9_12. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24264250
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: Structure, function, and drug discovery.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 May;111:400-414. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.157. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29305884 Review.
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as drug targets.Enzymes. 2020;48:321-350. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Enzymes. 2020. PMID: 33837708
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as drug targets in eukaryotic parasites.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2013 Nov 11;4(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2013.10.001. eCollection 2014 Apr. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2013. PMID: 24596663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for detecting aminoacylation and aminoacyl-tRNA editing in vitro and in cells.Isr J Chem. 2024 Sep;64(8-9):e202400009. doi: 10.1002/ijch.202400009. Epub 2024 May 6. Isr J Chem. 2024. PMID: 40066018 Free PMC article.
-
First comprehensive untargeted metabolomics study of suramin-treated Trypanosoma brucei: an integrated data analysis workflow from multifactor data modelling to functional analysis.Metabolomics. 2024 Feb 23;20(2):25. doi: 10.1007/s11306-024-02094-2. Metabolomics. 2024. PMID: 38393408
-
A Review of Antibacterial Candidates with New Modes of Action.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 11;10(10):3440-3474. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00218. Epub 2024 Jul 17. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39018341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

