Laboratory Experiment and Application Evaluation of a Bio-Nano-depressurization and Injection-Increasing Composite System in Medium-Low Permeability Offshore Reservoirs
- PMID: 37151548
- PMCID: PMC10157855
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00882
Laboratory Experiment and Application Evaluation of a Bio-Nano-depressurization and Injection-Increasing Composite System in Medium-Low Permeability Offshore Reservoirs
Abstract
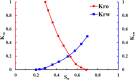
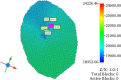
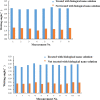
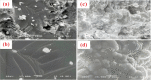
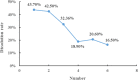
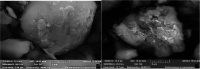
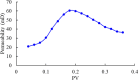
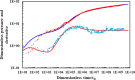
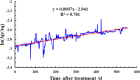
Given the high injection pressure and insufficient injection volume in the offshore oilfield, Bohai Oilfield has developed a bio-nano-depressurization and injection-increasing composite system solution (bio-nano-injection-increasing solution) composed of bio-surfactants, hydrophobic nano-polysilicon particles, and dispersant additives. In response to the current problems, a new type of bio-nano-depressurization and injection enhancement technology has been studied, which has multiple functions such as nano-scale inhibition and wetting reversal. The new technology has the technical advantages of efficient decompression, long-term injection, and wide adaptation. However, there is still a lack of optimization schemes and application effect prediction methods, which hinder the further popularization and application of the bio-nano-composite system solution. To solve this problem, this paper takes Well A1 in the Bohai Sea as an example to optimize the injection volume, concentration, and speed of the bio-nano-augmentation fluid and evaluates the application effect by using the proposed well testing, water absorption index, and numerical simulation methods. The research results show that the bio-nano-injection fluid can effectively improve the reservoir permeability and reduce the injection pressure. The application effect evaluation method proposed is reliable and can provide some reference for similar depressurization and injection-increasing technologies.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhou Y.-B.; He Y.-F.; Zhang W.; Zhang J.-L.; Yang L. Economic Limit Water Cut of Single Well in Offshore Waterflooding Oilfield. Lithol. Reservoirs 2019, 31, 130–134.
-
- Zhang Y.-L.; Liao X.-W.; Hu Y.; Li T.-L.; Su J.-C. Development Models for Offshore Heavy Oil Field in High Water Cut Stage. Lithol. Reservoirs 2018, 30, 120–126.
-
- Du H.-R.; Jiang S.-X.; Zhao W.-M.; Chen J.-F.; Miao B. Analysis on the regular of acid stimulation of low permeability sandstone reservoirs. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2008, 36, 61–63.
-
- Qinfeng D.; Shen C.; Wang Z.-H.; Gu C.-Y.; Shi L.-Y.; Fang H.-P. Experimental research on drag reduction of flow in micro channels of rocks using nano-particle adsorption method. Acta Pet. Sin. 2009, 30, 125–128. 10.7623/syxb200901027. - DOI
-
- Di Q.-F.; Li Z.-H.; Shi L.-Y.; Wu F.; Gu C.-Y.; Yu Z.-B. Effect of hydrophobic nanoparticles SiO2 on flow characteristics in microchannel. J. Univ. Pet., China 2009, 33, 109–111.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

