A novel approach for automatic segmentation of prostate and its lesion regions on magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 37152013
- PMCID: PMC10154598
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1095353
A novel approach for automatic segmentation of prostate and its lesion regions on magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Objective: To develop an accurate and automatic segmentation model based on convolution neural network to segment the prostate and its lesion regions.
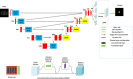
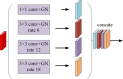
Methods: Of all 180 subjects, 122 healthy individuals and 58 patients with prostate cancer were included. For each subject, all slices of the prostate were comprised in the DWIs. A novel DCNN is proposed to automatically segment the prostate and its lesion regions. This model is inspired by the U-Net model with the encoding-decoding path as the backbone, importing dense block, attention mechanism techniques, and group norm-Atrous Spatial Pyramidal Pooling. Data augmentation was used to avoid overfitting in training. In the experimental phase, the data set was randomly divided into a training (70%), testing set (30%). four-fold cross-validation methods were used to obtain results for each metric.
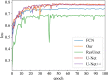
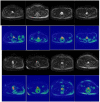
Results: The proposed model achieved in terms of Iou, Dice score, accuracy, sensitivity, 95% Hausdorff Distance, 86.82%,93.90%, 94.11%, 93.8%,7.84 for the prostate, 79.2%, 89.51%, 88.43%,89.31%,8.39 for lesion region in segmentation. Compared to the state-of-the-art models, FCN, U-Net, U-Net++, and ResU-Net, the segmentation model achieved more promising results.
Conclusion: The proposed model yielded excellent performance in accurate and automatic segmentation of the prostate and lesion regions, revealing that the novel deep convolutional neural network could be used in clinical disease treatment and diagnosis.
Keywords: U-Net; attention mechanism; convolution neural network; dense block; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Ren, Ren, Guo, Zhang, Luo, Ren, Tian, Li, Yuan, Hao, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ARPM-net: A novel CNN-based adversarial method with Markov random field enhancement for prostate and organs at risk segmentation in pelvic CT images.Med Phys. 2021 Jan;48(1):227-237. doi: 10.1002/mp.14580. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33151620
-
Deeply supervised 3D fully convolutional networks with group dilated convolution for automatic MRI prostate segmentation.Med Phys. 2019 Apr;46(4):1707-1718. doi: 10.1002/mp.13416. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30702759 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic segmentation of prostate cancer metastases in PSMA PET/CT images using deep neural networks with weighted batch-wise dice loss.Comput Biol Med. 2023 May;158:106882. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106882. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37037147
-
A dense residual U-net for multiple sclerosis lesions segmentation from multi-sequence 3D MR images.Int J Med Inform. 2023 Feb;170:104965. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2022.104965. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Int J Med Inform. 2023. PMID: 36580821
-
Convolutional neural network for automated mass segmentation in mammography.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Dec 9;21(Suppl 1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3521-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33297952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ProLesA-Net: A multi-channel 3D architecture for prostate MRI lesion segmentation with multi-scale channel and spatial attentions.Patterns (N Y). 2024 May 15;5(7):100992. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2024.100992. eCollection 2024 Jul 12. Patterns (N Y). 2024. PMID: 39081575 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Prediction of Muscle Invasion in Bladder Cancer Using Semi-Automatic Lesion Segmentation of MRI Compared with Manual Segmentation.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Nov 25;10(12):1355. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10121355. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38135946 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

