A new model based on gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to lymphocyte ratio and systemic immune-inflammation index can effectively predict the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation
- PMID: 37152021
- PMCID: PMC10157065
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1178123
A new model based on gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to lymphocyte ratio and systemic immune-inflammation index can effectively predict the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation
Abstract
Background: Liver transplantation (LT) is one of the most effective treatment modalities for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but patients with HCC recurrence after LT always have poor prognosis. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-lymphocyte ratio (GLR) and systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in terms of HCC recurrence after LT, based on which we developed a more effective predictive model.
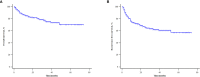
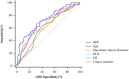
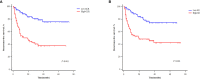
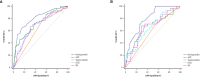
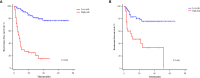
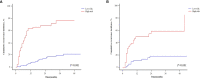
Methods: The clinical data of 325 HCC patients who had undergone LT were collected and analyzed retrospectively. The patients were randomly divided into a development cohort (n = 215) and a validation cohort (n = 110). Cox regression analysis was used to screen the independent risk factors affecting postoperative recurrence in the development cohort, and a predictive model was established based on the results of the multivariate analysis. The predictive values of GLR, SII and the model were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, which determined the cut-off value for indicating patients' risk levels. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and the competing-risk regression analysis were used to evaluate the predictive performance of the model, and the effectiveness of the model was verified further in the validation cohort.
Results: The recurrence-free survival of HCC patients after LT with high GLR and SII was significantly worse than that of patients with low GLR and SII (P<0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified GLR (HR:3.405; 95%CI:1.954-5.936; P<0.001), SII (HR: 2.285; 95%CI: 1.304-4.003; P=0.004), tumor number (HR:2.368; 95%CI:1.305-4.298; P=0.005), maximum tumor diameter (HR:1.906; 95%CI:1.121-3.242; P=0.017), alpha-fetoprotein level (HR:2.492; 95%CI:1.418-4.380; P=0.002) as independent risk factors for HCC recurrence after LT. The predictive model based on these risk factors had a good predictive performance in both the development and validation cohorts (area under the ROC curve=0.800, 0.791, respectively), and the performance of the new model was significantly better than that of single GLR and SII calculations (P<0.001). Survival analysis and competing-risk regression analysis showed that the predictive model could distinguish patients with varying levels of recurrence risk in both the development and validation cohorts.
Conclusions: The GLR and SII are effective indicators for evaluating HCC recurrence after LT. The predictive model based on these indicators can accurately predict HCC recurrence after LT and is expected to guide preoperative patient selection and postoperative follow-up.
Keywords: gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-lymphocyte ratio; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver transplantation; prediction; prognosis; recurrence; systemic immune-inflammation index.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Bi, Yang, Xie, Li, Yu, Zhang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive value of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to lymphocyte count ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion.BMC Cancer. 2020 Feb 18;20(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6628-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32070301 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic model for predicting recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with high systemic immune-inflammation index based on machine learning in a multicenter study.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1459740. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1459740. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39315112 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) is Useful to Predict Survival Outcomes in Patients After Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Hangzhou Criteria.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(1):293-301. doi: 10.1159/000489807. Epub 2018 May 11. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29768257
-
Challenges in Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Current Controversies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 2;16(17):3059. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173059. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Clues for Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Liver Transplantation.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023 Sep-Oct;13(5):804-812. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.02.006. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37693263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Low Albumin-Bilirubin Grade in TACE Combined with Ablation: A Random Forest Cox Predictive Model.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jul 8;11:1375-1388. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S465962. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39005969 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating Inflammatory Markers and Clinical Indicators into a Predictive Model of Single Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Primary Locoregional Treatments.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jun 13;11:1113-1125. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S465069. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38887683 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1007/s12094-025-04028-3. Online ahead of print. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40828354 Review.
-
Gamma-glutamyl transferase-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatectomy.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 Feb 27;17(2):98578. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.98578. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40061977 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

