Clonogenicity-based radioresistance determines the expression of immune suppressive immune checkpoint molecules after hypofractionated irradiation of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 37152024
- PMCID: PMC10157086
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.981239
Clonogenicity-based radioresistance determines the expression of immune suppressive immune checkpoint molecules after hypofractionated irradiation of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells
Abstract
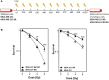
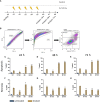
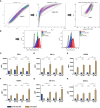
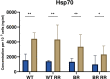
Only a subset of patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) benefits from a combination of radio- (RT) and immunotherapy. Therefore, we aimed to examine the impact of radioresistance and brain metastasizing potential on the immunological phenotype of TNBC cells following hypofractionated RT by analyzing cell death, immune checkpoint molecule (ICM) expression and activation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs). MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer tumor cells were used as model system. Apoptosis was the dominant cell death form of brain metastasizing tumor cells, while Hsp70 release was generally significantly increased following RT and went along with necrosis induction. The ICMs PD-L1, PD-L2, HVEM, ICOS-L, CD137-L and OX40-L were found on the tumor cell surfaces and were significantly upregulated by RT with 5 x 5.2 Gy. Strikingly, the expression of immune suppressive ICMs was significantly higher on radioresistant clones compared to their respective non-radioresistant ones. Although hypofractionated RT led to significant cell death induction and release of Hsp70 in all tumor cell lines, human monocyte-derived DCs were not activated after co-incubation with RT-treated tumor cells. We conclude that radioresistance is a potent driver of immune suppressive ICM expression on the surface of TNBC MDA-MB-231 cells. This mechanism is generally known to predominantly influence the effector phase, rather than the priming phase, of anti-tumor immune responses.
Keywords: breast cancer; dendritic cells; immune checkpoint molecules; radioresistance; radiotherapy; tumor cell death.
Copyright © 2023 Gehre, Meyer, Sengedorj, Grottker, Reichardt, Alomo, Borgmann, Frey, Fietkau, Rückert and Gaipl.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Hyperthermia and Radiotherapy Sequence on Cancer Cell Death and the Immune Phenotype of Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;14(9):2050. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092050. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565180 Free PMC article.
-
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy Upregulates Several Immune Checkpoint Molecules in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Independently of the HPV Status While ICOS-L Is Upregulated Only on HPV-Positive Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9114. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179114. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502022 Free PMC article.
-
Normofractionated irradiation and not temozolomide modulates the immunogenic and oncogenic phenotype of human glioblastoma cell lines.Strahlenther Onkol. 2023 Dec;199(12):1140-1151. doi: 10.1007/s00066-022-02028-8. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Strahlenther Onkol. 2023. PMID: 36480032 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on the Therapeutic Potentiality of PD-L1-Inhibiting MicroRNAs for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Toward Single-Cell Sequencing-Guided Biomimetic Delivery.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;12(8):1206. doi: 10.3390/genes12081206. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440380 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibition in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2022 Nov;22(11):1225-1238. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2022.2139240. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 36278877 Review.
Cited by
-
A 3D Co-Culture Scaffold Approach to Assess Spatially Fractionated Radiotherapy Bystander and Abscopal Immune Effects on Clonogenic Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 7;26(9):4436. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094436. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative G. Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, et al. . Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet (2011) 378(9804):1707–16. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61629-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ebctcg. McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane F, et al. . Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet (2014) 383(9935):2127–35. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

