AI diagnostic performance based on multiple imaging modalities for ovarian tumor: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37152032
- PMCID: PMC10160474
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1133491
AI diagnostic performance based on multiple imaging modalities for ovarian tumor: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: In recent years, AI has been applied to disease diagnosis in many medical and engineering researches. We aimed to explore the diagnostic performance of the models based on different imaging modalities for ovarian cancer.
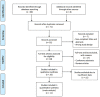
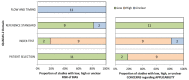
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Wanfang Database were searched. The search scope was all published Chinese and English literatures about AI diagnosis of benign and malignant ovarian tumors. The literature was screened and data extracted according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. Quadas-2 was used to evaluate the quality of the included literature, STATA 17.0. was used for statistical analysis, and forest plots and funnel plots were drawn to visualize the study results.
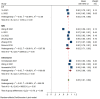
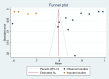
Results: A total of 11 studies were included, 3 of them were modeled based on ultrasound, 6 based on MRI, and 2 based on CT. The pooled AUROCs of studies based on ultrasound, MRI and CT were 0.94 (95% CI 0.88-1.00), 0.82 (95% CI 0.71-0.93) and 0.82 (95% Cl 0.78-0.86), respectively. The values of I2 were 99.92%, 99.91% and 92.64% based on ultrasound, MRI and CT. Funnel plot suggested no publication bias.
Conclusion: The models based on ultrasound have the best performance in diagnostic of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: AI; meta-analysis; ovarian cancer; systematic review; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2023 Ma, Huang, Chen, Zhang, Nie, He and Qi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indirect comparison of the diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/CT and MRI in differentiating benign and malignant ovarian or adnexal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 6;21(1):1080. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08815-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34615498 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of imaging differential diagnosis of benign and malignant ovarian tumors.Gland Surg. 2022 Feb;11(2):330-340. doi: 10.21037/gs-21-889. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 35284306 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence performance in image-based ovarian cancer identification: A systematic review and meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2022 Sep 17;53:101662. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101662. eCollection 2022 Nov. EClinicalMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36147628 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of indirect comparison between miRNA and ctDNA in diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5372-5382. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-2609. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. Retraction in: Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Apr;11(4):980. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-862. PMID: 35116384 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the recurrence of epithelial ovarian cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 7;12:1003465. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1003465. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36419900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and management of gynecologic cancer.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025 Apr 25:10.1002/ijgo.70094. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.70094. Online ahead of print. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 40277295
-
Ultrasound radiomics-based artificial intelligence model to assist in the differential diagnosis of ovarian endometrioma and ovarian dermoid cyst.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 8;11:1362588. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1362588. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38523908 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid artificial intelligence echogenic components-based diagnosis of adnexal masses on ultrasound.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17983. doi: 10.1002/mp.17983. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40665507 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Performance in Image-Based Cancer Identification: Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Apr 1;27:e53567. doi: 10.2196/53567. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40167239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christiansen F, Epstein EL, Smedberg E, Åkerlund M, Smith K, Epstein E. Ultrasound image analysis using deep neural networks for discriminating between benign and malignant ovarian tumors: comparison with expert subjective assessment. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol (2021) 57(1):155–63. doi: 10.1002/uog.23530 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources