A simplified non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy for the whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampus avoidance
- PMID: 37152035
- PMCID: PMC10155751
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1143564
A simplified non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy for the whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampus avoidance
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the feasibility of using a simplified non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy (NC-VMAT) and investigate its dosimetric advantages compared with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy (C-VMAT) for hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiation therapy (HA-WBRT).
Methods: Ten patients with brain metastase (BM) were included for HA-WBRT. Three treatment plans were generated for each case using IMRT, C-VMAT, and NC-VMAT, respectively.
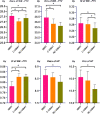
Results: The dosimetric results of the three techniques complied roughly with the RTOG 0933 criteria. After dose normalization, the V30Gy of whole brain planned target volume (WB-PTV) in all the plans was controlled at 95%. Homogeneity index (HI) of WB-PTV was significantly reduced in NC-VMAT (0.249 ± 0.017) over IMRT (0.265 ± 0.020, p=0.005) and C-VMAT (0.261 ± 0.014, p=0.020). In terms of conformity index (CI), NC-VMAT could provide a value of 0.821 ± 0.010, which was significantly superior to IMRT (0.788 ± 0.019, p<0.001). According to D2% of WB-PTV, NC-VMAT could provide a value of 35.62 ± 0.37Gy, significantly superior to IMRT (36.43 ± 0.65Gy, p<0.001). According to D50% of WB-PTV, NC-VMAT can achieve the lowest value of 33.18 ± 0.29Gy, significantly different from IMRT (33.47 ± 0.43, p=0.034) and C-VMAT (33.58 ± 0.37, p=0.006). Regarding D2%, D98%, and Dmean of hippocampus, NC-VMAT could control them at 15.57 ± 0.18Gy, 8.37 ± 0.26Gy and 11.71 ± 0.48Gy, respectively. D2% and Dmean of hippocampus for NC-VMAT was significantly lower than IMRT (D2%: 16.07 ± 0.29Gy, p=0.001 Dmean: 12.18 ± 0.33Gy, p<0.001) and C-VMAT (D2%: 15.92 ± 0.37Gy, p=0.009 Dmean: 12.21 ± 0.54Gy, p<0.001). For other organs-at-risk (OARs), according to D2% of the right optic nerves and the right lenses, NC-VMAT had the lowest values of 31.86 ± 1.11Gy and 7.15 ± 0.31Gy, respectively, which were statistically different from the other two techniques. For other organs including eyes and optic chiasm, NC-VMAT could achieve the lowest doses, different from IMRT statistically.
Conclusion: The dosimetry of the three techniques for HA-WBRT could roughly comply with the proposals from RTOG 0933. After dose normalization (D95%=30Gy), NC-VMAT could significantly improve dose homogeneity and reduce the D50% in the brain. Besides, it can reduce the D2% of the hippocampus, optic nerves, and lens. With this approach, an efficient and straightforward plan was accomplished.
Keywords: IMRT; VMAT; brain metastases; coplanar; hippocampal avoiding; noncoplanar; whole brain radiation therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Xue, Jin, Zhang, Zou, Sheng, Tang, Zhao, Yang, Tang, Lv and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A dosimetric comparison of non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy and non-coplanar fixed field intensity modulated radiation therapy in hippocampus-avoidance whole-brain radiation therapy with a simultaneous integrated boost for brain metastases.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 23;14:1428329. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1428329. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39917360 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for reduced radiation-induced toxicity using intensity-modulated arc therapy for whole-brain radiotherapy with hippocampal sparing.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 Sep 8;16(5):131–141. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i5.5587. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26699321 Free PMC article.
-
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy, coplanar volumetric-modulated arc, therapy, and noncoplanar volumetric-modulated arc therapy in, glioblastoma: A dosimetric comparison.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019 Dec;187:105573. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105573. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31706107
-
Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy under coplanar or noncoplanar VMAT.Med Dosim. 2023 Autumn;48(3):134-139. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Med Dosim. 2023. PMID: 37012163
-
Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy in hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14218. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14218. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38013656 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Delineation Errors Caused by Replication and Expansion Operations in Monaco.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241285961. doi: 10.1177/15330338241285961. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39311646 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of different head tilt angles in volumetric modulated arc therapy for hippocampus-avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 27;14:1415471. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1415471. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38993636 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of flattening filter free beams for hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy: a dosimetric and radiobiological analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 22;13:1290434. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1290434. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38074656 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Head Tilt Angles in Tomotherapy and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241281326. doi: 10.1177/15330338241281326. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39233627 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal sparing in whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: controversy, technology and the future.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 24;14:1342669. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1342669. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38327749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tabouret E, Chinot O, Metellus P, Tallet A, Viens P, Gonçalves A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: An overview. Anticancer Res (2012) 32(11):4655–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

