Bibliometric analysis of worldwide research trends on breast cancer about inflammation
- PMID: 37152044
- PMCID: PMC10154678
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1166690
Bibliometric analysis of worldwide research trends on breast cancer about inflammation
Abstract
Background: The most prevalent cancer and the second-leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women is breast cancer. Growing interest has been shown in recent years in learning more about the processes behind the development of breast cancer. It has been shown that persistent inflammation may play a significant role in the advancement of breast cancer. However, a comprehensive and objective analysis on the state of inflammation in breast cancer research is still lacking. This study was aim to undertake a bibliometric analysis of breast cancer research associated with inflammation between 2013 and 2022 in order to identify the trends, dynamics, and scientific outputs in the field.
Methods: From 2013 to 2022, original and review publications on breast cancer and inflammation-associated research were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database. To examine the position of yearly publications, journals, nations, institutions, and authors, we employed two bibliometric tools (CiteSpace and VOSviewer). After that, by examining keyword visualization and keyword bursts, we determined the hot research fields related to inflammation in breast cancer.
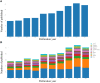
Results: we discovered 6902 publications regarding inflammation in breast cancer by using our retrieval approach. In terms of the number of publications, The United States ranked first in the global study, followed by China and Italy. In terms of institutions, the University of Texas System, UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, and University of California System are in the top 3 for the quantity of publications published. The most popular journal for this field research is "CANCERS." Ueno NT, Woodward WA, Cristofanilli M, and others have made significant contributions to the understanding of inflammation in breast cancer. In the end, we conducted a biclustering analysis on keywords and discovered three clusters that represent research hotspots.
Conclusion: According to the global trend, the research output of inflammation in breast cancer is increasing. The information provided in this article, including the cooperation network information of authors, nations, journals, and institutions, may help researchers to better understand hotspots and developing patterns in this discipline. At present, the focus of study gradually shifts from "phenotype study" to "therapeutic research". It is recommended to pay attention to the latest hot spots, such as targeted therapy, antimicrobial activity and nanoparticle.
Keywords: Breast cancer; VOSviewer; bibliometrics; hotspots; inflammation.
Copyright © 2023 Meng, Xu, Yang, Chen, Wang, Hu, Zheng and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research relating to minimally invasive spine surgery reported over the period 2000-2022.Digit Health. 2023 May 4;9:20552076231173562. doi: 10.1177/20552076231173562. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37163171 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Research on ultrasound-based radiomics: a bibliometric analysis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jul 1;14(7):4520-4539. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1867. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39022291 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on male osteoporosis: a neglected field deserves more attention.Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Oct 11;16(1):154. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-01016-2. Arch Osteoporos. 2021. PMID: 34632530 Review.
-
A bibliometric and visual analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1323115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323115. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38173726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of research trend of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer treatment: a bibliometric analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 19;16(1):1154. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02950-0. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40536693 Free PMC article.
-
Research status and trends of deep learning in colorectal cancer (2011-2023): Bibliometric analysis and visualization.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):103667. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.103667. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487952 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

