Dacarbazine-encapsulated solid lipid nanoparticles for skin cancer: physical characterization, stability, in-vivo activity, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry
- PMID: 37152046
- PMCID: PMC10160449
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1102269
Dacarbazine-encapsulated solid lipid nanoparticles for skin cancer: physical characterization, stability, in-vivo activity, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry
Abstract
Background: This study examined the use of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) to administer Dacarbazine (DTIC) to skin melanoma cells with minimal adverse effects. Melanoma is a tricky skin cancer to cure, and standard chemotherapy has many negative effects. Encapsulating DTIC in SLNs may allow the drug to target melanoma cells without harming healthy cells. The study developed and tested DTIC-loaded SLNs for skin melanoma treatment.
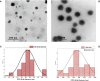
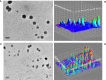
Methods: This study encapsulated Dacarbazine (DTIC) in solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). SLNs with reversed micelles were produced utilizing specified ratios of the surfactant Kolliphor® P188 and phosphatidylcholine. To track SLN drug localisation, gold nanoparticles were conjugated to the DTIC. Nanoparticle size and form were examined using DLS and TEM. These approaches ensured SLNs had the correct size and shape for drug delivery.
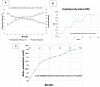
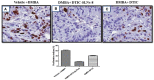
Significant findings: In the study, various parameters of the developed solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) were evaluated, including particle size, zeta potential, polydispersity index (PDI), entrapment efficacy, and cumulative drug permeation. The values for these parameters varied across the different formulations, with particle size ranging from 146 ± 4.71 nm to 715 ± 7.36 nm, zeta potential from -12.45 ± 2.78 mV to -30.78 ± 2.83 mV, PDI from 0.17 ± 0.013 to 0.51 ± 0.023, entrapment efficacy from 37.78 ± 2.78% to 87.45 ± 4.78%, and cumulative drug permeation from 117 ± 4.77 μg/cm2 to 275 ± 5.67 μg/cm2. To determine the optimal anti-cancer formulation, the DTIC-SLNs-8 nanoparticles were mixed with an optimized concentration of Gellan gum (0.01% w/v) and applied to DMBA-induced skin tumors in rats for six weeks, twice daily. Histopathology demonstrated that DTIC-SLNs-8-treated rats had less keratosis, inflammatory responses, and angiogenesis than free DTIC-treated rats. The development of SLNs may be a promising approach for melanoma treatment due to their improved drug retention over the skin. The optimised anti-cancer formulation DTIC-SLNs-8 showed improved efficacy with minimal side effects as compared to free DTIC.
Keywords: cancer; ehrlich ascetic carcinoma; melanoma; solid lipid nanoparticles; wistar rats.
Copyright © 2023 Bhattacharya and Sharma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Formulation, Characterization, and Evaluation of Eudragit-Coated Saxagliptin Nanoparticles Using 3 Factorial Design Modules.Molecules. 2022 Nov 3;27(21):7510. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217510. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364338 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical Characterization of Chitosan-Decorated Finasteride Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Drug Delivery.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 6;2022:7792180. doi: 10.1155/2022/7792180. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35971450 Free PMC article.
-
Solid lipid-based nanoparticulate system for sustained release and enhanced in-vitro cytotoxic effect of 5-fluorouracil on skin Melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 28;18(2):e0281004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281004. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36854019 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained release of piroxicam from solid lipid nanoparticle as an effective anti-inflammatory therapeutics in vivo.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017 Jan;43(1):55-66. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2016.1220563. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017. PMID: 27498809
-
Development of solid lipid nanoparticles-loaded drugs in parasitic diseases.Discov Nano. 2024 Jan 4;19(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s11671-023-03955-w. Discov Nano. 2024. PMID: 38175309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology as a Promising Method in the Treatment of Skin Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 10;25(4):2165. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042165. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Versatile Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) Using Design of Experiments (DoE)-Part II: Incorporation and Stability of Butamben with Different Surfactants.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 27;16(7):863. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070863. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pankaj R. Research, formulation and evaluation of implantable drug delivery system of dacarbazine by using hydrophilic polymer. J Pharm Sci Res (2020) 12(3):405–12. doi: 10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i11.20070 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

