Perioperative, oncologic, and functional outcomes of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for special types of renal tumors (hilar, endophytic, or cystic): an evidence-based analysis of comparative outcomes
- PMID: 37152053
- PMCID: PMC10157041
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1178592
Perioperative, oncologic, and functional outcomes of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for special types of renal tumors (hilar, endophytic, or cystic): an evidence-based analysis of comparative outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to perform a pooled analysis to compare the outcomes of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) between complex tumors (hilar, endophytic, or cystic) and non-complex tumors (nonhilar, exophytic, or solid) and evaluate the effects of renal tumor complexity on outcomes in patients undergoing RAPN.
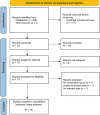
Methods: Four databases were systematically searched, including Science, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, to identify relevant studies published in English up to December 2022. Review Manager 5.4 was used for statistical analyses and calculations. The study was registered with PROSPERO (Registration number: CRD42023394792).
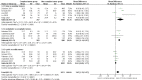
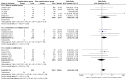
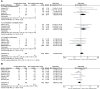
Results: In total, 14 comparative trials, including 3758 patients were enrolled. Compared to non-complex tumors, complex tumors were associated with a significantly longer warm ischemia time (WMD 3.67 min, 95% CI 1.78, 5.57; p = 0.0001), more blood loss (WMD 22.84 mL, 95% CI 2.31, 43.37; p = 0.03), and a higher rate of major complications (OR 2.35, 95% CI 1.50, 3.67; p = 0.0002). However, no statistically significant differences were found between the two groups in operative time, length of stay, transfusion rates, conversion to open nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy rates, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline, intraoperative complication, overall complication, positive surgical margins (PSM), local recurrence, and trifecta achievement.
Conclusions: RAPN can be a safe and effective procedure for complex tumors (hilar, endophytic, or cystic) and provides comparable functional and oncologic outcomes to non-complex tumors.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=394792, identifier CRD42023394792.
Keywords: cystic renal tumors; endophytic renal tumors; meta-analysis; renal hilar tumors; robot-assisted partial nephrectomy.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Li, Wu, Du, Tan, Zhang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Impacts of completely endophytic renal masses on perioperative, oncologic, and functional outcomes in robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 25;14:1444477. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1444477. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39512766 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for technically challenging renal tumors (completely endophytic and hilar): a systematic review and meta-analysis of perioperative, oncological, and functional outcomes.J Robot Surg. 2025 Apr 10;19(1):144. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02307-3. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40208473
-
Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for hilar tumors: perioperative outcomes.Urology. 2013 Jun;81(6):1246-51. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2012.10.072. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Urology. 2013. PMID: 23601446
-
Perioperative, functional, and oncologic outcomes of robot-assisted versus open partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors (RENAL score ≥ 7): an evidence-based analysis.J Robot Surg. 2023 Aug;17(4):1247-1258. doi: 10.1007/s11701-023-01565-3. Epub 2023 Mar 13. J Robot Surg. 2023. PMID: 36913056 Review.
-
Perioperative, functional, and oncologic outcomes of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy versus open partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 10;13:1283935. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1283935. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38273858 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From sutureless to standard: a comprehensive analysis of conversion rates in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.BMC Urol. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12894-024-01578-6. BMC Urol. 2024. PMID: 39198764 Free PMC article.
-
Value of the urine culture and antibiotic prophylaxis before partial nephrectomy in cancer (UroCCR n°107 - NephroBacte).World J Urol. 2025 Apr 19;43(1):235. doi: 10.1007/s00345-025-05619-z. World J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40252185
-
Immune-Based and Novel Therapies in Variant Histology Renal Cell Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;17(2):326. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020326. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Achieving trifecta outcomes in robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy within a fellowship training centre.J Robot Surg. 2024 Jul 2;18(1):275. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-01941-7. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 38954074
-
Evaluating the learning curve of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy with the cumulative sum method.J Robot Surg. 2025 Jul 24;19(1):418. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02599-5. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40707816
References
-
- Chang KD, Abdel Raheem A, Kim KH, Oh CK, Park SY, Kim YS, et al. . Functional and oncological outcomes of open, laparoscopic and robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: a multicentre comparative matched-pair analyses with a median of 5 years' follow-up. BJU Int (2018) 122(4):618–26. doi: 10.1111/bju.14250 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

