Outbreak of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae at a Portuguese university hospital: Epidemiological characterization and containment measures
- PMID: 37152080
- PMCID: PMC10158887
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000186
Outbreak of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae at a Portuguese university hospital: Epidemiological characterization and containment measures
Abstract
Background: KPC-producing K pneumoniae (KPC-Kp) is a public health problem with important clinical and epidemiological implications. We describe an outbreak of KPC-Kp at vascular surgery and neurosurgery wards in a central hospital in Porto, Portugal.
Methods: A case of KPC-Kp was considered to be a patient positive for KPC-Kp with strong epidemiological plausibility of having acquired this microorganism in the affected wards and/or with genetic relationship ≥92% between KPC-Kp isolates. Active surveillance cultures (ASCs) and real-time polymerase chain reaction were used for the detection of carbapenemase genes through rectal swab in a selected population. Molecular analysis was performed using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis at the National Reference Laboratory. Patient risk factors were collected from the electronic medical record system. Information regarding outbreak containment strategy was collected from the Infection Control Unit records.
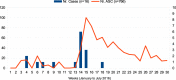
Results: Of the 16 cases, 11 (69%) were identified through active screening, representing 1.4% of the total 766 ASCs collected. The most frequent risk factors identified were previous admission (63%), antibiotic exposure in the past 6 months (50%), and immunodepression (44%). The length of stay until KPC-Kp detection was high (0-121 days, mean 35.6), as was the total length of stay (5-173 days, mean 56.6). Three patients (19%) were infected by KPC-Kp, 2 of whom died. One previously colonized patient died later because of KPC-Kp infection.
Conclusions: Multifactorial strategy based on contact precautions (with patient and healthcare professional cohorts) and ASC, as well as Antibiotic Stewardship Program reinforcement, allowed to contain this KPC-Kp outbreak.
Keywords: KPC-producing K pneumoniae; active surveillance cultures; antimicrobial resistance; carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae; contact precautions; outbreak.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of PBJ-Associação Porto Biomedical/Porto Biomedical Society. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clonal replacement of epidemic KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a hospital in China.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 May 23;17(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2467-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28535790 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for KPC-producing Enterobacteriaceae acquisition and infection in a healthcare setting with possible local transmission: a case-control study.J Hosp Infect. 2017 Jun;96(2):111-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.02.010. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Hosp Infect. 2017. PMID: 28389093
-
Genomic Epidemiology of an Endoscope-Associated Outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC)-Producing K. pneumoniae.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 4;10(12):e0144310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144310. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26637170 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: the role of infection control.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Jan 29;76(Suppl 1):i4-i11. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa492. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33534880 Review.
-
How to manage KPC infections.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2020 May 14;7:2049936120912049. doi: 10.1177/2049936120912049. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32489663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tackling Carbapenem Resistance and the Imperative for One Health Strategies-Insights from the Portuguese Perspective.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;13(6):557. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060557. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Rosa FG, Corcione S, Cavallo R, Di Perri G, Bassetti M. Critical issues for Klebsiella pneumoniae KPC-carbapenemase producing K. pneumoniae infections: a critical agenda. Future Microbiol. 2015;10:283–294. - PubMed
-
- Nordemann P, Poirel L. The difficult-to-control spread of carbapenemase producers among Enterobacteriaceae worldwide. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20:821–830. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
