Comparison between all-on-four and all-on-six treatment concepts on stress distribution for full-mouth rehabilitation using three-dimensional finite element analysis: A biomechanical study
- PMID: 37152467
- PMCID: PMC10159094
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_278_22
Comparison between all-on-four and all-on-six treatment concepts on stress distribution for full-mouth rehabilitation using three-dimensional finite element analysis: A biomechanical study
Abstract
Purpose: The current study intended to provide a comparison of biomechanical behaviors of two different treatment concepts for full-mouth rehabilitation with dental implants placed according to the "All-on-four" concept and "All-on-six" concept with analysis of the stress patterns of the implant support system using three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA).
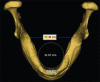
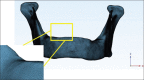
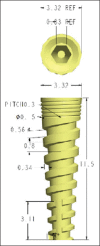
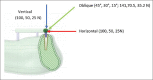
Materials and methods: The edentulous mandible was treated with two different implant designs. "All-on-Four" implant placement concept was used in Model 1 with two central axial implants and two distally tilted implants at 17° and in Model 2, "All-on-Six" concept was applied with six vertically placed implants. Individual vertical and horizontal load of 100 N and oblique load of 141 N at 45° was applied to all implants. To evaluate and compare the results in terms of maximum principal stress, we used FEA.
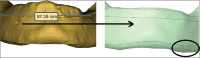
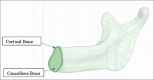
Results: All-on-six showed smaller maximum principal stress values on the cortical bone and implants. However, maximum principal stress values obtained on trabecular bone was smaller in the All-on-four design for vertical and horizontal loading conditions.
Conclusions: The All-on-six approach showed more favorable biomechanical behavior.
Keywords: All-on-four; all-on-six; finite element analysis; maximum principal stress; tilted implants.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Society of Periodontology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Klee de Vasconcellos D, Bottino MA, Saad PA, Faloppa F. A new device in immediately loaded implant treatment in the edentulous mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21:615–22. - PubMed
-
- Maló P, Rangert B, Nobre M. “All-on-Four”immediate-function concept with Brånemark system implants for completely edentulous mandibles: A retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5(Suppl 1):2–9. - PubMed
-
- Federick DR, Caputo AA. Effects of overdenture retention designs and implant orientations on load transfer characteristics. J Prosthet Dent. 1996;76:624–32. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe F, Hata Y, Komatsu S, Ramos TC, Fukuda H. Finite element analysis of the influence of implant inclination, loading position, and load direction on stress distribution. Odontology. 2003;91:31–6. - PubMed
-
- Clelland NL, Gilat A. The effect of abutment angulation on stress transfer for an implant. J Prosthodont. 1992;1:24–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
