A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
- PMID: 37152476
- PMCID: PMC10156454
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5731248
A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Abstract
Background: Apically extruded debris (AED) is an inherent concern during root canal treatment for both endodontists and general practitioners. The present study investigates the AED of the novel R-Motion single-file reciprocating system compared to standard single reciprocating and multifile rotary systems.
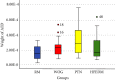
Materials and methods: Fifty-six moderately curved palatal roots of upper maxillary first molars were selected for the present study. The samples were then divided randomly into four groups (n = 14)- Group I: R-motion (RM), Group II: WaveOne Gold (WOG), Group III: ProTaper Next (PTN), and Group IV: HyFlex EDM (HFEDM). The researcher has modified Myers and Montgomery's method to simulate human body temperature. Vials were used to collect debris and weighted using a 0.00001 sensitive balance before and after instrumentation. The instrumentation of all experimented groups was done at 37°C, terminated at master apical file #25. An auto syringe with a side vented needle was used to deliver 8 ml of deionized water for irrigation of each sample during preparation. Vials were stored in a dry sealed desiccator which contained CaSO4 crystals, for 24 hr before weighing. The weight of the collected debris was obtained by subtracting the preinstrumentation weight from the postinstrumentation weight for each vial. The Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests were performed to analyse the statistical difference in the amount of debris between the tested groups at a 0.05 significance level.
Results: The RM system produced less debris extrusion than all tested groups, with a significant difference between the former and the WOG and the PTN systems. However, WOG, PTN, and HFEDM showed no statistically significant difference in the amount of AED.
Conclusion: All tested groups produced apical debris in different amounts. The RM produced substantially less AED than WOG and PTN. Meanwhile, WOG, PTN, and HFEDM caused a comparable amount of AED.
Copyright © 2023 Farah B. Al-Saffar and Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- De Deus G., Silva E. J. N. L., Souza E., Versiani M. A., Zuolo M. Shaping for Cleaning the Root Canals: A Clinical-Based Strategy . Springer Cham; 2022. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

