Liuwei Dihuang formula ameliorates chronic stress-induced emotional and cognitive impairments in mice by elevating hippocampal O-GlcNAc modification
- PMID: 37152609
- PMCID: PMC10157057
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1134176
Liuwei Dihuang formula ameliorates chronic stress-induced emotional and cognitive impairments in mice by elevating hippocampal O-GlcNAc modification
Abstract
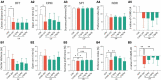
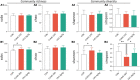
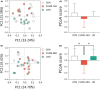
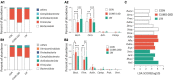
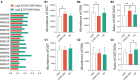
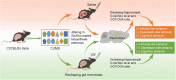
A substantial body of evidence has indicated that intracerebral O-linked N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine (O-GlcNAc), a generalized post-translational modification, was emerging as an effective regulator of stress-induced emotional and cognitive impairments. Our previous studies showed that the Liuwei Dihuang formula (LW) significantly improved the emotional and cognitive dysfunctions in various types of stress mouse models. In the current study, we sought to determine the effects of LW on intracerebral O-GlcNAc levels in chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) mice. The dynamic behavioral tests showed that anxiety- and depression-like behaviors and object recognition memory of CUMS mice were improved in a dose-dependent manner after LW treatment. Moreover, linear discriminate analysis (LEfSe) of genera abundance revealed a significant difference in microbiome among the study groups. LW showed a great impact on the relative abundance of these gut microbiota in CUMS mice and reinstated them to control mouse levels. We found that LW potentially altered the Uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) biosynthesis process, and the abundance of O-GlcNAcase (OGA) and O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) in CUMS mice, which was inferred using PICRUSt analysis. We further verified advantageous changes in hippocampal O-GlcNAc modification of CUMS mice following LW administration, as well as changes in the levels of OGA and OGT. In summary, LW intervention increased the levels of hippocampal O-GlcNAc modification and ameliorated the emotional and cognitive impairments induced by chronic stress in CUMS mice. LW therefore could be considered a potential prophylactic and therapeutic agent for chronic stress.
Keywords: Liuwei Dihuang formula; O-GlcNAc; O-GlcNAc transferase; O-GlcNAcase; gut microbiota.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Wang, Liu, Wang, Xiao and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson S. T., Paschos G. K. (2019). The role for the microbiome in the regulation of the circadian clock and metabolism. Nutr. Epigenom. 14 231–248.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

