The Effect of Number of Visits, Use of Solvent and Gutta-percha Removal Technique on Postoperative Pain following Nonsurgical Endodontic Retreatment; A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 37152852
- PMCID: PMC10155107
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v18i2.39945
The Effect of Number of Visits, Use of Solvent and Gutta-percha Removal Technique on Postoperative Pain following Nonsurgical Endodontic Retreatment; A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The nonsurgical endodontic retreatment (NERT) is the first choice of dental ministration when primary/initial endodontic treatment fails. The present study aimed to investigate the presence of postoperative pain (POP) after NERT in permanent asymptomatic teeth as well as possible factors associated with POP.
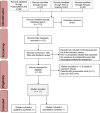
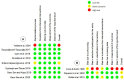
Materials and methods: A comprehensive search of literature was performed in Pubmed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus and Web of Science databases, up to January 2023; including randomized clinical trials and prospective studies. The risk of bias was assessed with RoB 2.0 and ROBINS-I tools. Subgroups analyses were conducted to evaluate the differences in the incidence or level of POP between the number of visits, the use/not use of solvent, the removal technique of gutta-percha, and the period of POP analysis. Mean differences and confidence intervals (CI) of 95% were used as measures of effect, and meta-regression was used along with subgroup analysis. The certainty of evidence was assessed using GRADE, and the probability value of <0.05 was considered significant.
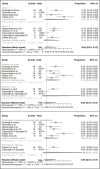
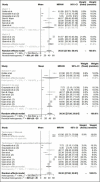
Results: Twenty-four studies were selected, with thirteen included in the meta-analysis. There was a statistical difference between the incidence of POP after 24 h (95% CI, 0.28 to 0.52) and one week (95% CI, 0.02 to 0.13) from the endodontic retreatment (P<0.01). However, there was no statistical difference between different techniques, number of visits and use of solvent (P>0.05) in the same period. In addition, the certainty of evidence was very low.
Conclusions: Post-operative pain is a common response to NERT, independent of the retreatment technique(s) applied, number of visits and use of solvent(s); with very low certainty of evidence as well as low risk of bias. Moreover, the current analysis showed a (very) serious risk of inconsistency and imprecision. However, POP was significantly reduced within 1 week of the NERT.
Keywords: Endodontic Retreatment; Endodontics; Meta-analysis; Postoperative Pain; Systematic Review.
Conflict of interest statement
‘None declared’.
Figures


References
-
- Siqueira JF Jr, Rôças IN, Ricucci D, Hülsmann M. Causes and management of post-treatment apical periodontitis. Br Dent J. 2014;216(6):305–12. - PubMed
-
- Ricucci D, Russo J, Rutberg M, Burleson JA, Spångberg LS. A prospective cohort study of endodontic treatments of 1,369 root canals: results after 5 years. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112(6):825–42. - PubMed
-
- Chércoles-Ruiz A, Sánchez-Torres A, Gay-Escoda C. Endodontics, Endodontic Retreatment, and Apical Surgery Versus Tooth Extraction and Implant Placement: A Systematic Review. J Endod. 2017;43(5):679–86. - PubMed
-
- Lazarski MP, Walker WA, Flores CM, Schindler WG, Hargreaves KM. Epidemiological evaluation of the outcomes of nonsurgical root canal treatment in a large cohort of insured dental patients. J Endod. 2001;27(12):791–6. - PubMed
-
- Torabinejad M, White SN. Endodontic treatment options after unsuccessful initial root canal treatment: Alternatives to single-tooth implants. J Am Dent Assoc. 2016;147(3):214–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
