Predictive dynamical modeling and stability of the equilibria in a discrete fractional difference COVID-19 epidemic model
- PMID: 37153140
- PMCID: PMC10140436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rinp.2023.106467
Predictive dynamical modeling and stability of the equilibria in a discrete fractional difference COVID-19 epidemic model
Abstract
The SARSCoV-2 virus, also known as the coronavirus-2, is the consequence of COVID-19, a severe acute respiratory syndrome. Droplets from an infectious individual are how the pathogen is transmitted from one individual to another and occasionally, these particles can contain toxic textures that could also serve as an entry point for the pathogen. We formed a discrete fractional-order COVID-19 framework for this investigation using information and inferences from Thailand. To combat the illnesses, the region has implemented mandatory vaccination, interpersonal stratification and mask distribution programs. As a result, we divided the vulnerable people into two groups: those who support the initiatives and those who do not take the influence regulations seriously. We analyze endemic problems and common data while demonstrating the threshold evolution defined by the fundamental reproductive quantity . Employing the mean general interval, we have evaluated the configuration value systems in our framework. Such a framework has been shown to be adaptable to changing pathogen populations over time. The Picard Lindelöf technique is applied to determine the existence-uniqueness of the solution for the proposed scheme. In light of the relationship between the and the consistency of the fixed points in this framework, several theoretical conclusions are made. Numerous numerical simulations are conducted to validate the outcome.
Keywords: 26A33; 26A51; 26D07; 26D10; 26D15; Discrete fractional operator; Equilibrium points; Existence and uniqueness; Fractional difference equation; Local and global stability.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
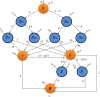
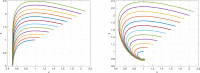
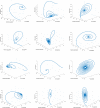
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modeling and simulation of fractional order COVID-19 model with quarantined-isolated people.Math Methods Appl Sci. 2021 May 30;44(8):6389-6405. doi: 10.1002/mma.7191. Epub 2021 Jan 17. Math Methods Appl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33821071 Free PMC article.
-
New computations of the fractional worms transmission model in wireless sensor network in view of new integral transform with statistical analysis; an analysis of information and communication technologies.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 13;10(16):e35955. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35955. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39687853 Free PMC article.
-
A fractional-order model describing the dynamics of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with nonsingular kernel.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021 May;146:110859. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110859. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021. PMID: 33776249 Free PMC article.
-
Fractional-Order Epidemic Model for Measles Infection.Scientifica (Cairo). 2024 Oct 10;2024:8997302. doi: 10.1155/2024/8997302. eCollection 2024. Scientifica (Cairo). 2024. PMID: 39421686 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical system of COVID-19 disease model: Existence, uniqueness, numerical and sensitivity analysis.MethodsX. 2023;10:102045. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102045. Epub 2023 Jan 28. MethodsX. 2023. PMID: 36742367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brauer F., Castillo-Chavez C., Feng Z. Springer-Verlag; New York: 2019. Mathematical models in epidemiology.
-
- Ratnayake R., Finger F., Azman A.S., Lantagne D., Funk S., Edmunds W.J., et al. Highly targeted spatiotemporal interventions against cholera epidemics, 2000–19: a scoping review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Area I., Ndaırou F., Nieto J.J., Silva C.J., Torres D.F.M. Ebola model and optimal control with vaccination constraints. J Ind Manag Optim. 2018;14:427–446.
-
- Maayah B., Arqub O.A., Alnabulsi S. Numerical solutions and geometric attractors of a fractional model of the cancer-immune based on the Atangana–Baleanu–Caputo derivative and the reproducing kernel scheme. Chinese J Phys. 2022:80. doi: 10.1016/j.cjph.2022.10.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
