Exploration of multifaceted molecular mechanism of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in pathogenesis of various diseases
- PMID: 37153428
- PMCID: PMC10160752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15644
Exploration of multifaceted molecular mechanism of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in pathogenesis of various diseases
Abstract
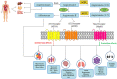
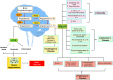
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a homolog of ACE (a transmembrane bound dipeptidyl peptidase enzyme). ACE2 converts angiotensinogen to the heptapeptide angiotensin-(1-7). ACE2 and its product, angiotensin-(1-7), have counteracting effects against the adverse actions of other members of renin-angiotensin system (RAS). ACE2 and its principal product, angiotensin-(1-7), were considered an under recognized arm of the RAS. The COVID-19 pandemic brought to light this arm of RAS with special focus on ACE2. Membrane bound ACE2 serves as a receptor for SARS-CoV-2 viral entry through spike proteins. Apart from that, ACE2 is also involved in the pathogenesis of various other diseases like cardiovascular disease, cancer, respiratory diseases, neurodegenerative diseases and infertility. The present review focuses on the molecular mechanism of ACE2 in neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, cardiovascular disease, infertility and respiratory diseases, including SARS-CoV-2. This review summarizes unveiled roles of ACE2 in the pathogenesis of various diseases which further provides intriguing possibilities for the use of ACE2 activators and RAS modulating agents for various diseases.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; Cancer; Neurodegenerative diseases; Renin-angiotensin system; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Hooper N.M., Lambert D.W., Turner A.J. Discovery and characterization of ACE2–a 20-year journey of surprises from vasopeptidase to COVID-19. Clin. Sci. 2020;134:2489–2501. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

