In Vitro Activities and Inoculum Effects of Cefiderocol and Aztreonam-Avibactam against Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae
- PMID: 37154758
- PMCID: PMC10269523
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00569-23
In Vitro Activities and Inoculum Effects of Cefiderocol and Aztreonam-Avibactam against Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae
Abstract
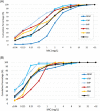
Cefiderocol and aztreonam-avibactam (ATM-AVI) both had activity against carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacilli, including those that produce metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs). We compared the in vitro activities and inoculum effects of these antibiotics against carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE), especially MBL-producing isolates. The MICs of cefiderocol and ATM-AVI were determined using broth microdilution method for a 2016 to 2021 collection of Enterobacteriaceae isolates which produced MBL, KPC, or OXA-48-like carbapenemases. MICs with high bacteria inoculum were also evaluated for susceptible isolates. A total of 195 CPE were tested, including 143 MBL- (74 NDM, 42 IMP, and 27 VIM), 38 KPC-, and 14 OXA-48-like-producing isolates. The susceptible rates of MBL-, KPC-, and OXA-48-like producers to cefiderocol were 86.0%, 92.1%, and 92.9%, respectively, and that to ATM-AVI were 95.8%, 100%, and 100%, respectively. NDM producers displayed lower susceptibility and higher MIC50s/MIC90s of cefiderocol (78.4%, 2/16 mg/L) than IMP (92.9%, 0.375/4 mg/L) and VIM (96.3%, 1/4 mg/L) producers. NDM- and VIM-producing Escherichia coli showed lower susceptibility to ATM-AVI (77.3% and 75.0%, respectively) compared to MBL-CPE of other species (100% susceptible). Inoculum effects for cefiderocol and ATM-AVI were observed among 95.9% and 95.2% of susceptible CPE, respectively. A switch from susceptible to resistant category was observed in 83.6% (143/171) of isolates for cefiderocol and 94.7% (179/189) for ATM-AVI. Our results revealed that NDM-producing Enterobacteriaceae had lower susceptibility to cefiderocol and ATM-AVI. Prominent inoculum effects on both antibiotics were observed for CPE, which suggested a risk of microbiological failure when they were used for CPE infections with high bacteria burden. IMPORTANCE The prevalence of infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae is increasing worldwide. Currently, therapeutic options for metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae remain limited. We demonstrated that clinical metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae isolates were highly susceptible to cefiderocol (86.0%) and aztreonam-avibactam (ATM-AVI) (95.8%). However, inoculum effects on cefiderocol and ATM-AVI were observed for over 90% of susceptible carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) isolates. Our findings highlight a potential risk of microbiological failure when using monotherapy with cefiderocol or ATM-AVI to treat severe CPE infection.
Keywords: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; cefiderocol; inoculum effect; metallo-β-lactamase; β-lactam and β-lactamase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Grundmann H, Glasner C, Albiger B, Aanensen DM, Tomlinson CT, Andrasević AT, Cantón R, Carmeli Y, Friedrich AW, Giske CG, Glupczynski Y, Gniadkowski M, Livermore DM, Nordmann P, Poirel L, Rossolini GM, Seifert H, Vatopoulos A, Walsh T, Woodford N, Monnet DL, European Survey of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (EuSCAPE) Working Group . 2017. Occurrence of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli in the European survey of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (EuSCAPE): a prospective, multinational study. Lancet Infect Dis 17:153–163. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30257-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sandfort M, Hans JB, Fischer MA, Reichert F, Cremanns M, Eisfeld J, Pfeifer Y, Heck A, Eckmanns T, Werner G, Gatermann S, Haller S, Pfennigwerth N. 2022. Increase in NDM-1 and NDM-1/OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany associated with the war in Ukraine, 2022. Euro Surveill 27. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.50.2200926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

