Ling Zhi-8, a fungal immunomodulatory protein in Ganoderma lucidum, alleviates CPT-11-induced intestinal injury via restoring claudin-1 expression
- PMID: 37155145
- PMCID: PMC10449289
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204695
Ling Zhi-8, a fungal immunomodulatory protein in Ganoderma lucidum, alleviates CPT-11-induced intestinal injury via restoring claudin-1 expression
Abstract
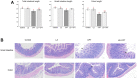
CPT-11 (Irinotecan) remains an important chemotherapeutic agent against various solid tumors nowadays. Potential adverse effects, especially gastrointestinal toxicities, are the main limiting factor for its clinical utility. Ling Zhi-8 (LZ-8), a fungal immunomodulatory protein in Ganoderma lucidum mycelia, has potential for drug development due to its multiple bioactivities and functions. This study aimed to explore the influence of LZ-8 on CPT-11-treated IEC-6 cells in vitro and on mice with CPT-11-induced intestinal injury in vivo. The mechanism through which LZ-8 exerted its protective effects was also investigated. In the in vitro study, the viability and claudin-1 expression of IEC-6 cells decreased gradually with increasing concentrations of CPT-11, but LZ-8 treatment had no obvious influence on their viability, morphology, and claudin-1 expression. Pretreatment of LZ-8 significantly improved CPT-11-decreased cell viability and claudin-1 expression in IEC-6 cells. In mice with CPT-11-induced intestinal injury, LZ-8 treatment could ameliorate symptoms and mitigate intestinal damage. Meanwhile, LZ-8 restored claudin-1 expression in the intestinal membranes in CPT-11-treated mice. Collectively, our results demonstrated the protective effects of LZ-8 against CPT-11 damage in both IEC-6 cells and mice. LZ-8 can restore claudin-1 expression in intestinal cells following CPT-11 treatment, suggesting the role of claudin-1 in the scenario.
Keywords: CPT-11; Ganoderma lucidum; Ling Zhi-8; claudin-1; irinotecan.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Reishi Protein LZ-8 Induces FOXP3(+) Treg Expansion via a CD45-Dependent Signaling Pathway and Alleviates Acute Intestinal Inflammation in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:513542. doi: 10.1155/2013/513542. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23864893 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides PS-G and protein LZ-8 from Reishi (Ganoderma lucidum) exhibit diverse functions in regulating murine macrophages and T lymphocytes.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Aug 11;58(15):8535-44. doi: 10.1021/jf100914m. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20681640
-
Pathological Changes in APP/PS-1 Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease Treated with Ganoderma Lucidum Preparation.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2017 Aug 20;39(4):552-561. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.04.015. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28877835 English.
-
Anti-osteoporosis Effect of Ganoderma (Lingzhi) by Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1182:263-269. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9421-9_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31777023 Review.
-
Ganoderma lucidum: a potent pharmacological macrofungus.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009 Dec;10(8):717-42. doi: 10.2174/138920109789978757. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19939212 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome study of dikaryotic and monokaryotic mycelia reveals the transfer between biological processes contributing to dikaryon growth advantage of the medicinal fungus Ganoderma lucidum.BMC Genomics. 2025 Aug 1;26(1):711. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11905-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40751175 Free PMC article.
-
Fufang Taizishen Granules Attenuate Chemotherapy-Induced Intestinal Mucositis by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Amino Acid Metabolism.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 11;13(8):e70789. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70789. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40801049 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in intestinal aging: From underlying mechanisms to therapeutic strategies.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Jul;15(7):3372-3403. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.011. Epub 2025 May 22. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40698139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

