Effect Measure Modification by Birth Weight on the Association Between Overweight or Obesity and Hypertension in Children and Adolescents
- PMID: 37155182
- PMCID: PMC10167596
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.0799
Effect Measure Modification by Birth Weight on the Association Between Overweight or Obesity and Hypertension in Children and Adolescents
Plain language summary
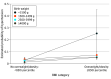
This cross-sectional study examines the prevalence of hypertension among children and adolescents with low, very low, normal, or high birth weight.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Decoding the Association Between Body Composition in Preterm Birth and Hypertension in Childhood.JAMA Pediatr. 2023 Nov 1;177(11):1238-1239. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3516. JAMA Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37695618 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, et al. . 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: methods and development. Vital Health Stat 11. 2002;(246):1-190. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al. ; Subcommittee on Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children . Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20171904. doi:10.1542/peds.2017-1904 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical