Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek
- PMID: 37156916
- PMCID: PMC10869269
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01773-0
Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek
Abstract
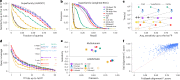
As structure prediction methods are generating millions of publicly available protein structures, searching these databases is becoming a bottleneck. Foldseek aligns the structure of a query protein against a database by describing tertiary amino acid interactions within proteins as sequences over a structural alphabet. Foldseek decreases computation times by four to five orders of magnitude with 86%, 88% and 133% of the sensitivities of Dali, TM-align and CE, respectively.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

