MicroRNA-22-3p Regulates the Apoptosis of Lens Epithelial Cells Through Targeting KLF6 in Diabetic Cataracts
- PMID: 37159192
- PMCID: PMC10179635
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.12.5.9
MicroRNA-22-3p Regulates the Apoptosis of Lens Epithelial Cells Through Targeting KLF6 in Diabetic Cataracts
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify novel abnormally expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) and their downstream target in diabetic cataract (DC).
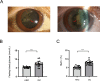
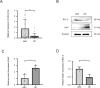
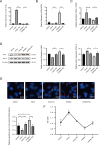
Methods: General feature, fasting blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, and type A1c (HbA1c) expression level of patients were collected. DC capsular tissues were obtained from patients and the lens cells (HLE-B3) exposed to different concentrations of glucose were used to simulate the model in vitro. Both mimic and inhibitor of miR-22-3p were transferred into HLE-B3 to up- and downregulate miR-22-3p expression, respectively. The cellular apoptosis was evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), Western blot, and immunofluorescence. The downstream target gene of miR-22-3p was identified by dual luciferase reporter.
Results: In DC capsules and HLE-B3 under hyperglycemia, miR-22-3p showed a significant downward trend. The expression of BAX was upregulated and the BCL-2 was downregulated following high glucose. The expression of BAX was significantly down- or upregulated in HLE-B3 cells following transfection of mimic or inhibitor of miR-22-3p, respectively. Conversely, BCL-2 was significantly increased or decreased. Dual luciferase reporter assay showed that miR-22-3p directly targeted Krüppel Like Factor 6 (KLF6) to regulate cell apoptosis. In addition, the expression of KLF6 were significantly up- or downregulated following transfection of inhibitor or mimic of miR-22-3p.
Conclusions: This study suggested that miR-22-3p could inhibit lens apoptosis by targeting KLF6 directly under high glucose condition. The miR-22-3p/KLF6 signal axis may provide novel insights into the pathogenesis of DC.
Translational relevance: Differential expression of miR-22-3p may account for the pathogenesis of DC and lead to a new therapeutic strategy for DC.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


References
-
- Ang MJ, Afshari NA.. Cataract and systemic disease: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021; 49(2): 118–127. - PubMed
-
- Lee CM, Afshari NA. The global state of cataract blindness. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2017; 28(1): 98–103. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg MJ, Bamba S. Diabetic cataracts. Dis Mon. 2021; 67(5): 101134. - PubMed
-
- Kumar PA, Reddy PY, Srinivas PN, et al. .. Delay of diabetic cataract in rats by the antiglycating potential of cumin through modulation of alpha-crystallin chaperone activity. J Nutr Biochem. 2009; 20(7): 553–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

