Accurate Identification of Leishmania Parasites in Sand Flies by Polymorphism Analysis of Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit 2 Gene Using Polymerase Chain Reaction and Quantitative PCR-High Resolution Melting Techniques in Iranian Border with Iraq
- PMID: 37159596
- PMCID: PMC10163367
- DOI: 10.18502/jad.v16i4.12085
Accurate Identification of Leishmania Parasites in Sand Flies by Polymorphism Analysis of Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit 2 Gene Using Polymerase Chain Reaction and Quantitative PCR-High Resolution Melting Techniques in Iranian Border with Iraq
Abstract
Background: Firmly identification of Leishmania in Phlebotomus papatasi and understanding of natural transmission cycles of parasites in sand flies are important for treatment and local control.
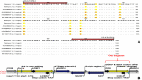
Methods: Modified and developed method of High Resolution Melting (HRM) as a preferable technique was employed to accurate identification of Leishmania in sand flies from Iranian border with Iraq, by targeting cytochrome oxidase II (COII) gene and designing suitable primers. PCR products cloned into pTG19-T vector, then purified plasmid concentration was measured at 260 and 280nm wavelength. The melting curve plots were generated and DNA sequences were analyzed using Sequencher 3.1.1, CLC Main Workbench 5.5, MEGA 6, DnaSP5.10.01 and MedCalc® version 13.3.3 soft wares.
Results: Among about 3000 collected sand flies, 89 female Ph. papatasi were identified and two with L. major. In amplified fragment of COII gene among 611bp, 452bp had no genetic variations with low polymorphic sites (P= 0.001) and high synonymous (79.8%) as compare to non-synonymous sites (20.2%). Leishmania major was discriminated in Ph. papatasi with 0.84 °C melting temperature (Tm) and unique curve based on thermodynamic differences was an important criterion using HRM technique.
Conclusion: Subsequent war in Iraq made a high risk habitat for parasites transmission. It is important to discover accurate diagnostic procedures for leishmaniasis control.
Keywords: Cloning; Cytochrome oxidase II; qPCR-HRM.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement The authors declare there is no conflict of interests.
Figures






References
-
- Ghafari SM, Fotouhi-Ardakani R, Parvizi P. (2020a) Designing and developing a high-resolution melting technique for accurate identification of Leishmania species by targeting amino acid permease 3 and cytochrome oxidase II genes using real-time PCR and in silico genetic evaluation. Acta Trop. 211: 105626. - PubMed
-
- Parvizi P, Ready PD. (2008) Nested PCRs and sequencing of nuclear ITS-rDNA fragments detect three Leishmania species of gerbils in sand flies from Iranian foci of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. Trop Med Int Health. 13(9): 1159–1171. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
