Korean Society of Heart Failure Guidelines for the Management of Heart Failure: Treatment
- PMID: 37161681
- PMCID: PMC10172201
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2023.0047
Korean Society of Heart Failure Guidelines for the Management of Heart Failure: Treatment
Abstract
The Korean Society of Heart Failure (KSHF) guidelines aim to provide physicians with evidence-based recommendations for the management of patients with heart failure (HF). After the first introduction of the KSHF guidelines in 2016, newer therapies for HF with reduced ejection fraction, HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction, and HF with preserved ejection fraction have since emerged. The current version has been updated based on international guidelines and research data on Korean patients with HF. Herein, we present Part II of these guidelines, which comprises treatment strategies to improve the outcomes of patients with HF.
Keywords: Guideline; Heart failure; Pharmacotherapy; Treatment.
Copyright © 2023. The Korean Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

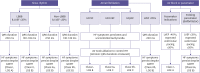

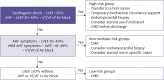

References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3599–3726. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79:e263–e421. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

